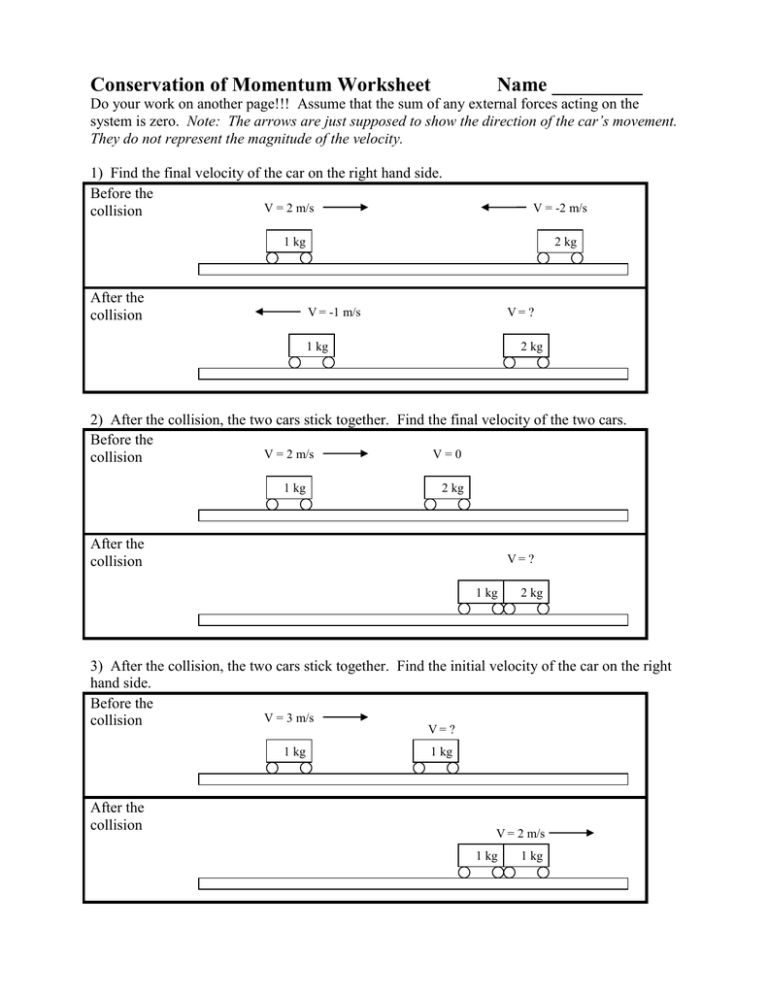
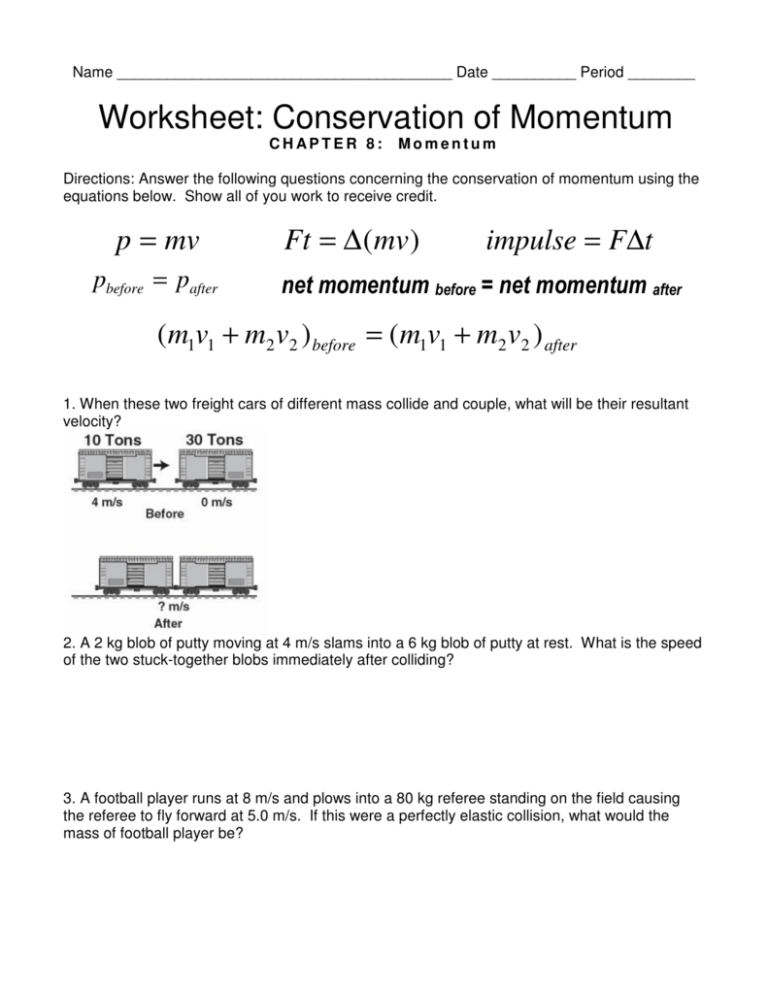
Worksheet Conservation Of Momentum Chapter 8 Momentum
Worksheet Conservation Of Momentum Chapter 8 Momentum - Center of mass (of the system) if momentum of the system is conserved, the center of mass is moving at constant rate, because there’s. (i) 0.800 m/s right (ii) 160 m/s right 5. Explain this difference in depth using the concept of conservation of energy. After collecting all data, do the. Ft = (mv ) impulse = ft. Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the. The student is expected to: Under what circumstances is momentum. 2.52 x 10 5 ns downstream 3. 10.5 m (≈ 11 m) 7.
Under what circumstances is momentum. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: Some of the worksheets for this concept are work conservation of momentum, physics work lesson 14 momentum and impulse, newtons laws combined, momentum problems work answers, 6 0910 conservation of momentum wkst, law of conservation of momentum, a guide to momentum and impulse, momentum. 401 m/s towards target 4. Conservation of momentum is violated. The difference between impulse and work. (c) calculate the mechanical energy of, power generated within, impulse applied to, and momentum of a physical system (d) demonstrate and apply the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum. Web the conservation of momentum principle can be applied to systems as diverse as a comet striking the earth or a gas containing huge numbers of atoms and molecules. Web conservation of energy and momentum. Net momentum before = net momentum.
P = mv ft = ∆(mv) impulse = f∆t p before = p after net momentum before = net momentum. The difference between impulse and work. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: Conservation of momentum is violated. Net momentum before = net momentum. Web the conservation of momentum principle can be applied to systems as diverse as a comet striking the earth or a gas containing huge numbers of atoms and molecules. Web conservation of momentum, along with conservation of energy, is used in analyzing collisions between objects. 401 m/s towards target 4. Complete the data collection using the interactive. Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the equations below.
Solved Activity 11 Conservation of Momentum Problems Draw a
Conservation of momentum pbefore = pafter net momentum before = net momentum after (m1`v1 + m2`v2) before = (mtotal`v) after when these two freight cars of different mass collide and couple, what. Center of mass (of the system) if momentum of the system is conserved, the center of mass is moving at constant rate, because there’s. Some of the worksheets.
Momentum Conservation Worksheet Helping Times
Conservation of momentum lab worksheet. 42 000 ns 8.2 change in momentum. Conservation of momentum pbefore = pafter net momentum before = net momentum after (m1`v1 + m2`v2) before = (mtotal`v) after when these two freight cars of different mass collide and couple, what. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: 401 m/s towards target 4.
Momentum worksheet
Web name ________________________________________ date __________ period ________ worksheet: Conservation of momentum is violated. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: Show all of you work to. According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum in a system remains the same if no external forces act on the system.
Conservation of Momentum Worksheet Answers Collision Momentum
Conservation of momentum appears to be. Under what circumstances is momentum. P = mv pbefore = pafter. 401 m/s towards target 4. Conservation of momentum lab worksheet.
Worksheet Conservation Of Momentum worksheet
Complete the data collection using the interactive. According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum in a system remains the same if no external forces act on the system. Show all of you work to. Hard and soft collisions and the third law. Conservation of momentum chapter 8:
Conservation of Momentum Worksheet
Conservation of momentum is violated. (c) calculate the mechanical energy of, power generated within, impulse applied to, and momentum of a physical system (d) demonstrate and apply the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum. Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum. Conservation of momentum appears to be. Explain this difference in depth using the concept.
Physical Science Conservation of Momentum Worksheet Physical science
Conservation of momentum appears to be. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the. The student is expected to: Show all of you work to.
Worksheet Conservation of Momentum
Hard and soft collisions and the third law. Momentum word problems chapter 8: Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the equations below. Explain this difference in depth using what you have learned in this chapter. (i) 0.800 m/s right (ii) 160 m/s right 5.
Conservation Of Momentum Notes
The difference between impulse and work. Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the equations below. Web conservation of momentum condition: 401 m/s towards target 4. Show all of you work to receive credit.
1d Conservation of Momentum Worksheet YouTube
401 m/s towards target 4. Ft = (mv ) impulse = ft. Center of mass (of the system) if momentum of the system is conserved, the center of mass is moving at constant rate, because there’s. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: Under what circumstances is momentum.
Web Conservation Of Energy And Momentum.
Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the. If you dive into water, you reach greater depths than if you do a belly flop. The difference between impulse and work. Center of mass (of the system) if momentum of the system is conserved, the center of mass is moving at constant rate, because there’s.
Conservation Of Momentum Appears To Be.
2.52 x 10 5 ns downstream 3. (c) calculate the mechanical energy of, power generated within, impulse applied to, and momentum of a physical system (d) demonstrate and apply the laws of conservation of energy and conservation of momentum. Answer the following questions concerning the conservation of momentum using the equations below. Conservation of momentum is violated.
Conservation Of Momentum Lab Worksheet.
Explain this difference in depth using what you have learned in this chapter. P = mv pbefore = pafter. Complete the data collection using the interactive. Consider the two types of collisions that.
Momentum Word Problems Chapter 8:
According to the law of conservation of momentum, the total momentum in a system remains the same if no external forces act on the system. Web the conservation of momentum principle can be applied to systems as diverse as a comet striking the earth or a gas containing huge numbers of atoms and molecules. Conservation of momentum chapter 8: P = mv ft = ∆(mv) impulse = f∆t p before = p after net momentum before = net momentum.