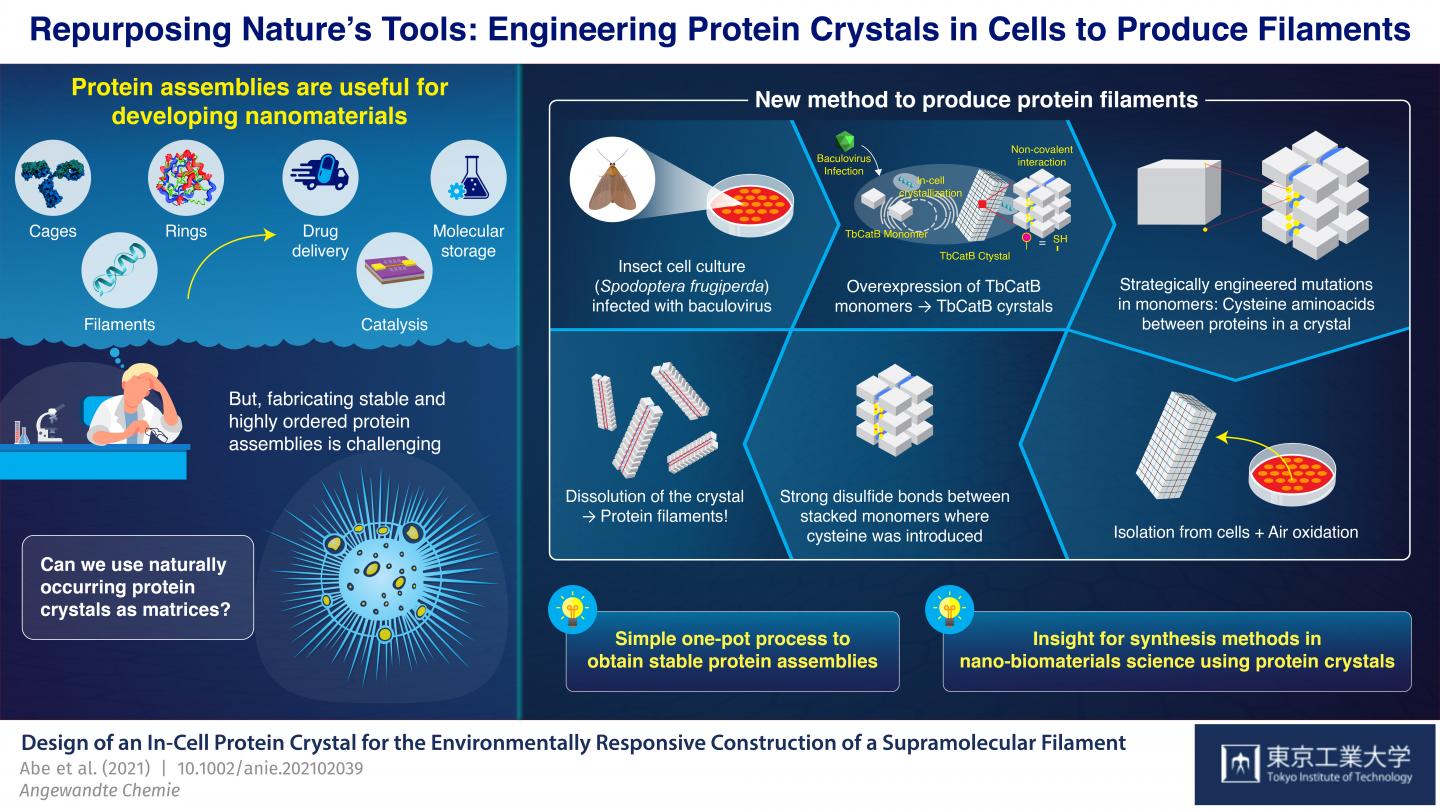
Which Protein Filaments Are Bundled Together To Form Cilia
Which Protein Filaments Are Bundled Together To Form Cilia - Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Actin filaments are one of the most abundant proteins in all mammalian cells. Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled together to form cilia? Web actin filaments occur in a cell in the form of meshwork or bundles of parallel fibres. Web in eukaryotes, there are three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton: Actin filaments are organized into. Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. Filamin is lacking in some types. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta.
Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled together to form cilia? Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Web in eukaryotes, there are three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton: Actin filaments are organized into. Web in biology, a protein filament is a long chain of protein monomers, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella.[1] protein filaments form together to make the cytoskeleton. Web actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. Actin filaments are one of the most abundant proteins in all mammalian cells. Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders.
Web microtubules are the protein filaments which are bundled together to form cilia and flagella. They join two actin filaments together to. They help in controlling the shape of the cell and also adhere the cell to the substrate. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Cilia are cellular structures composed of microtubules, specifically the protein filaments called microtubules, that are bundled together. Here, we'll examine each type of filament, as. Web they play a leading role not only in muscle cells: Web in biology, a protein filament is a long chain of protein monomers, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella.[1] protein filaments form together to make the cytoskeleton. Web actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. Web the cilia and flagella are made of protein filaments that are called microtubules doublets.
Muscle Anatomy Stock Illustration Image 46887626
Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin. They help in controlling the shape of the cell and also adhere the cell to the substrate. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled together to form cilia? These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders.
Coloured TEM of protein filaments in Alzheimer's Stock Image M108
Here, we'll examine each type of filament, as. Web in eukaryotes, there are three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton: Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin. Web actin is a globular protein that polymerizes (joins together many small molecules) to form long filaments. Web the eukaryotic flagellum shares many characteristics with the eukaryotic motile.
Thin Filaments in Skeletal Muscle Fibers • Definition & Function
Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled together to form cilia? Web the cilia and flagella are made of protein filaments that are called microtubules doublets. Web actin filaments occur in a cell in the form of meshwork or bundles of parallel fibres. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. These microtubules doublets are.
Bundled Protein Filaments Win Popular Vote in Nikon Small World
They join two actin filaments together to. Web in biology, a protein filament is a long chain of protein monomers, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella.[1] protein filaments form together to make the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta. Web in eukaryotes, there are three types of protein fibers.
Scientists design protein filaments that snap themselves together
Actin filaments are one of the most abundant proteins in all mammalian cells. Cilia are cellular structures composed of microtubules, specifically the protein filaments called microtubules, that are bundled together. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Here, we'll examine each type of filament, as. They join two actin filaments together to.
InCell Nano3D Printer Synthesizing Stable Filaments from inCell
Actin filaments are organized into. Web in biology, a protein filament is a long chain of protein monomers, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella.[1] protein filaments form together to make the cytoskeleton. They help in controlling the shape of the cell and also adhere the cell to the substrate. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. Actin.
Three major protein filaments make up the cell cytoskeleton
Web in biology, a protein filament is a long chain of protein monomers, such as those found in hair, muscle, or in flagella.[1] protein filaments form together to make the cytoskeleton. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. They join two actin filaments together to. Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled together to form.
Modification sites of thin filament proteins at the Zdisc. a The
Here, we'll examine each type of filament, as. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. Web in eukaryotes, there are three types of protein fibers in the cytoskeleton: Filamin is lacking in some types. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta.
Tau Protein Filament (SPR463)
Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta. Web actin filaments occur in a cell in the form of meshwork or bundles of parallel fibres. Web question 7 of 32 3.0/ 3.0 points which protein filaments are bundled.
Nucleus Overview Biology Ease
Actin filaments are organized into. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. Web microtubules are the protein filaments which are bundled together to form cilia and flagella. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta. They join two actin filaments together to.
They Join Two Actin Filaments Together To.
Web the cilia and flagella are made of protein filaments that are called microtubules doublets. Cilia are cellular structures composed of microtubules, specifically the protein filaments called microtubules, that are bundled together. Cilia are absent in bacteria and archaea. Because each actin subunit faces in the same direction, the actin.
Web In Biology, A Protein Filament Is A Long Chain Of Protein Monomers, Such As Those Found In Hair, Muscle, Or In Flagella.[1] Protein Filaments Form Together To Make The Cytoskeleton.
Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules. They help in controlling the shape of the cell and also adhere the cell to the substrate. Web actin filaments occur in a cell in the form of meshwork or bundles of parallel fibres. The filigree structures form an.
Web Question 7 Of 32 3.0/ 3.0 Points Which Protein Filaments Are Bundled Together To Form Cilia?
Web the eukaryotic flagellum shares many characteristics with the eukaryotic motile cilium [ 5 ], with each having an axonemal structure that consists of nine microtubule doublets that. Actin filaments are organized into. These microtubules doublets are hollow cylinders. Here, we'll examine each type of filament, as.
Web Actin Is A Globular Protein That Polymerizes (Joins Together Many Small Molecules) To Form Long Filaments.
Web microtubules are the protein filaments which are bundled together to form cilia and flagella. Microtubules are microscopic hollow tubes made of the proteins alpha and beta. Web they play a leading role not only in muscle cells: Actin filaments are one of the most abundant proteins in all mammalian cells.