Statics Chapter 3
Statics Chapter 3 - Web statics definition, the branch of mechanics that deals with bodies at rest or forces in equilibrium. Web 1 introduction to statics 2 forces and other vectors 3 equilibrium of particles 4 moments and static equivalence 5 rigid body equilibrium 6 equilibrium of structures 7 centroids and centers of. [noun, plural in form but singular or plural in construction] mechanics dealing with the relations of forces that produce equilibrium among material bodies. Equilibrium of a particle of the book static of rigid bodies by hibbeler. Web access vector mechanics for engineers: See our solution for question 1rp from chapter 3 from hibbeler's engineering mechanics. Statics 12th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Statics 14th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Subscribe my channel for more solutions! Web statics and mechanics of materials 3rd edition isbn:
Standard score and deviation score. Web statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque acting on a physical system that does not experience an acceleration, but rather, is in static equilibrium with its. The objectives of this chapter are: Statics and dynamics 12th edition chapter 3 solutions now. Statics 1st edition chapter 3 solutions now. [noun, plural in form but singular or plural in construction] mechanics dealing with the relations of forces that produce equilibrium among material bodies. Web statics and mechanics of materials 3rd edition isbn: To show how to add forces and resolve. Engineering statics by hibbeler 14th edition chapter 3: Statics 12th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.
Statics and dynamics 12th edition chapter 3 solutions now. Statics 14th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Web access vector mechanics for engineers: See our solution for question 1rp from chapter 3 from hibbeler's engineering mechanics. 9781260446418 alternate isbns david mazurek, e. Web statics and mechanics of materials 3rd edition isbn: Subscribe my channel for more solutions! Web this is an itemized solution manual for problem exercises chapter 3: Web 3.3 equilibrium for points and rigid bodies. Dewolf textbook solutions verified chapter 2:
Statics Review Part 3 YouTube
Our resource for vector mechanics for engineers:. Engineering statics by hibbeler 14th edition chapter 3: Dewolf textbook solutions verified chapter 2: Web statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque acting on a physical system that does not experience an acceleration, but rather, is in static equilibrium with its. P (.
Chapter 3 Cont FLUID STATICS HYDROSTATIC FORCES AND
Standard score and deviation score. Statics of particles page 26: Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! Subscribe my channel for more solutions! Web engineering statics by meriam and kraige!
Statics Videos Chapter 3 part 4 YouTube
Standard score and deviation score. Statics and dynamics, 14th edition. Subscribe my channel for more solutions! [noun, plural in form but singular or plural in construction] mechanics dealing with the relations of forces that produce equilibrium among material bodies. The objectives of this chapter are:
ME 273 Statics Chapter 3.4 YouTube
Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! 9781260446418 alternate isbns david mazurek, e. Subscribe my channel for more solutions! Engineering statics by hibbeler 14th edition chapter 3: Web access vector mechanics for engineers:
Engineering Mechanics By Hibbeler 14Th Edition proudnews.my.id
Web this is an itemized solution manual for problem exercises chapter 3: Statics and dynamics 12th edition chapter 3 solutions now. Dewolf textbook solutions verified chapter 2: Statics 12th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Subscribe my channel for more solutions!
Statics Chapter 3 lesson 11 YouTube
Web engineering statics by meriam and kraige! Dewolf textbook solutions verified chapter 2: Johnston, ferdinand beer, john t. 3.7 center of gravity and centroids. Statics 1st edition chapter 3 solutions now.
Statics chapter 2 YouTube
P ( c) = 542 5. Web access vector mechanics for engineers: Web engineering statics by meriam and kraige! Dewolf textbook solutions verified chapter 2: Web 1 introduction to statics 2 forces and other vectors 3 equilibrium of particles 4 moments and static equivalence 5 rigid body equilibrium 6 equilibrium of structures 7 centroids and centers of.
13,14 NOTE IS STUDYING STATICS CHAPTER 3 IN THIS
Johnston, ferdinand beer, john t. See our solution for question 1rp from chapter 3 from hibbeler's engineering mechanics. Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! Web statics and mechanics of materials 3rd edition isbn: X = x 1 +x 2 ++ x n n = 1 n ∑ n i=1 x.
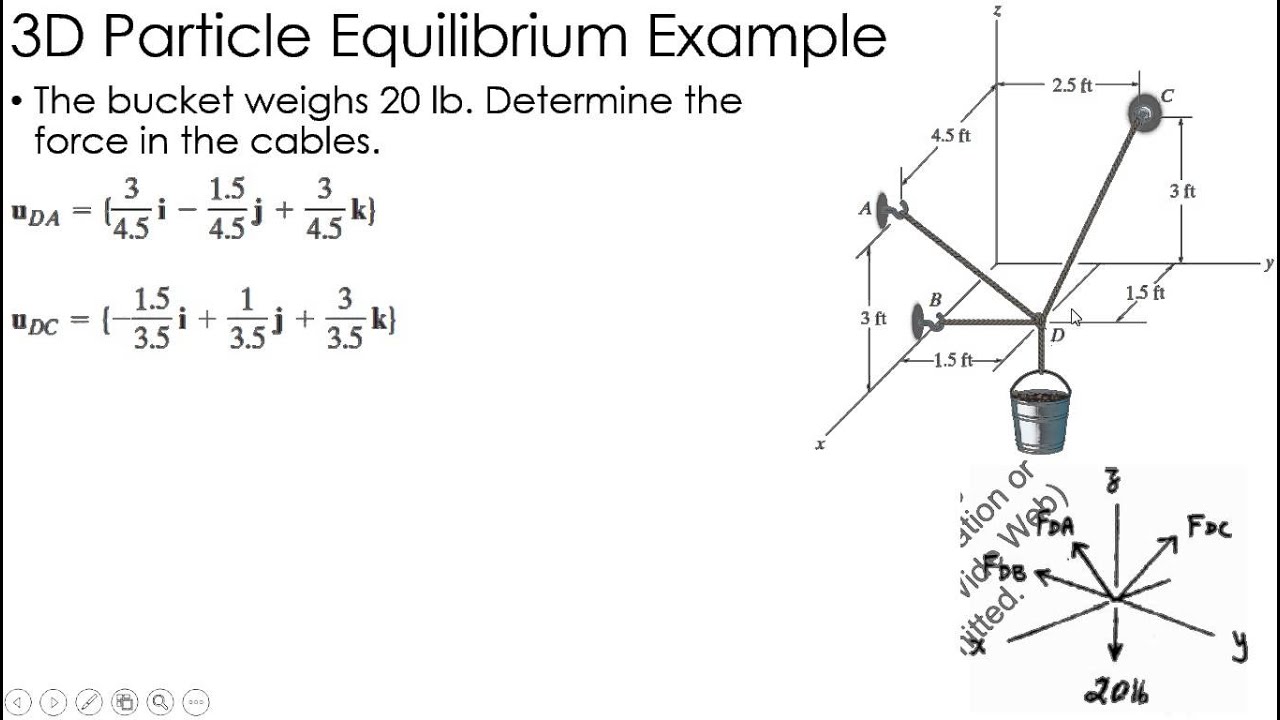
Static equilibrium 3d examples turboxoler
Johnston, ferdinand beer, john t. Statics 14th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Statics and dynamics 12th edition chapter 3 solutions now. 9781260446418 alternate isbns david mazurek, e. Web statics and mechanics of materials 3rd edition isbn:
Solved Chapter 3 Problem 110RP Solution Statics And Mechanics Of
Web statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque acting on a physical system that does not experience an acceleration, but rather, is in static equilibrium with its. Our solutions are written by chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality! Equilibrium of a particle of the book.
Web Engineering Statics By Meriam And Kraige!
The objectives of this chapter are: Web in this chapter, we look at several statistical measures used to describe data and draw statistical inferences. Review problems exercise 1 exercise 2 exercise 3. Our resource for vector mechanics for engineers:.
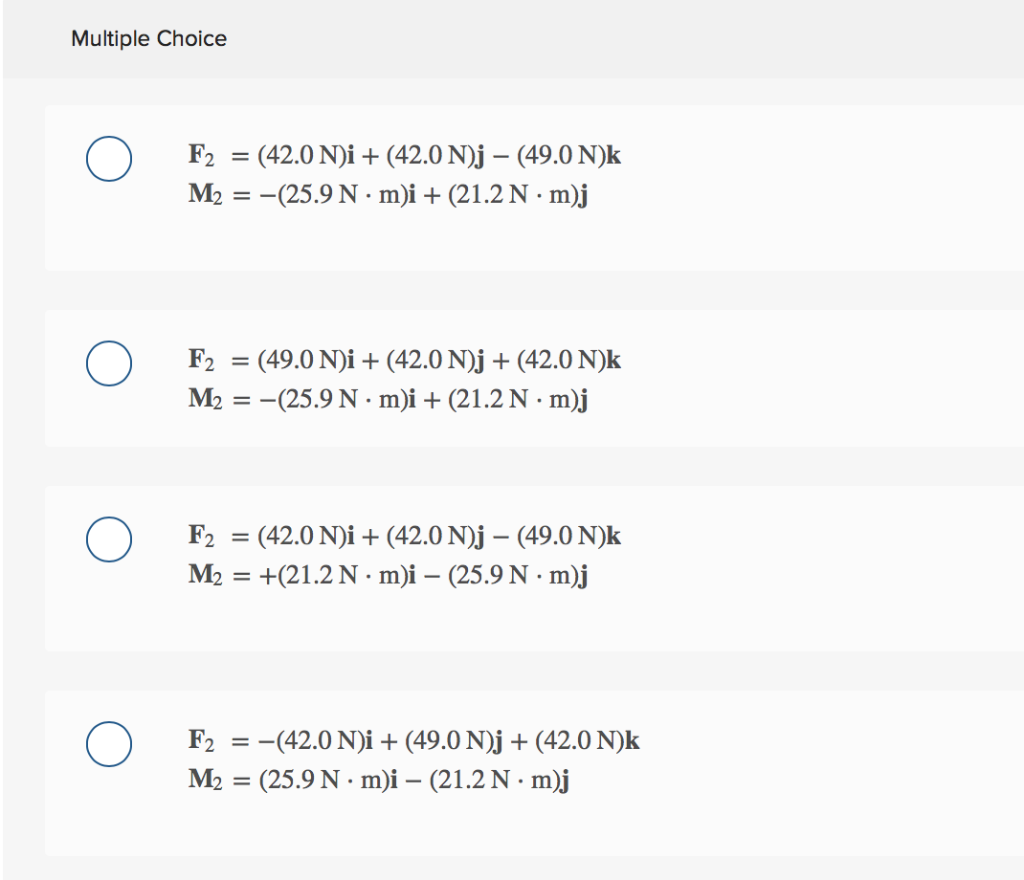
Equilibrium Of A Particle Of The Book Static Of Rigid Bodies By Hibbeler.
Web this is an itemized solution manual for problem exercises chapter 3: Standard score and deviation score. To show how to add forces and resolve. Statics 1st edition chapter 3 solutions now.
X = X 1 +X 2 ++ X N N = 1 N ∑ N I=1 X I (3…
P ( c) = 542 5. Web 1 introduction to statics 2 forces and other vectors 3 equilibrium of particles 4 moments and static equivalence 5 rigid body equilibrium 6 equilibrium of structures 7 centroids and centers of. See our solution for question 1rp from chapter 3 from hibbeler's engineering mechanics. Statics 14th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems.
Statics And Dynamics 12Th Edition Chapter 3 Solutions Now.
3.7 center of gravity and centroids. P ( l′) = p ( s) p ( m or s) p ( f and l) p ( m | l) p ( l | m) p ( s | f) p ( f | l) p ( f or l) p ( m and s) p ( f) 3. Statics 12th edition, you’ll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. [noun, plural in form but singular or plural in construction] mechanics dealing with the relations of forces that produce equilibrium among material bodies.