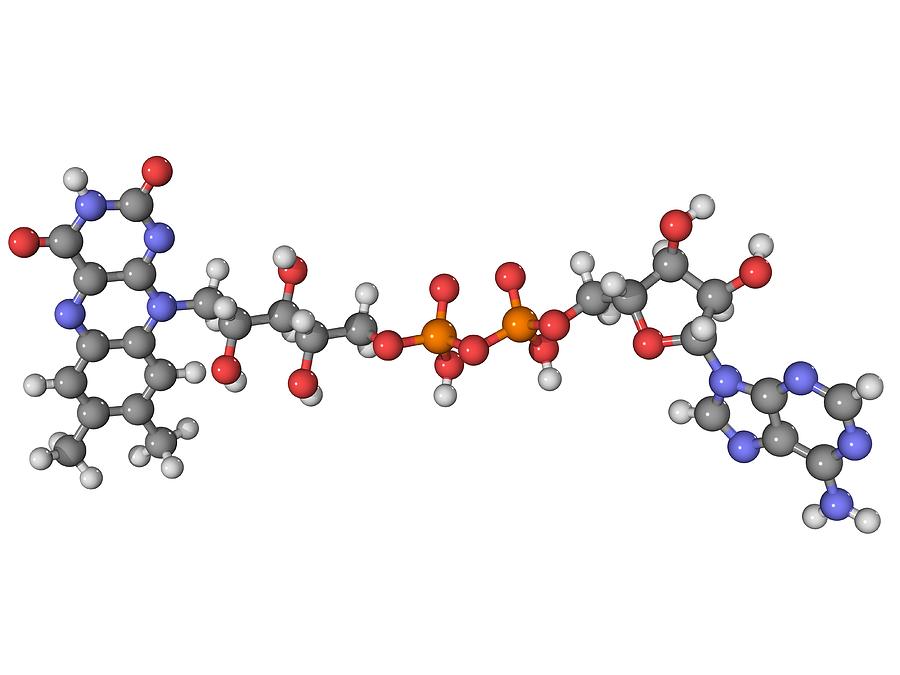
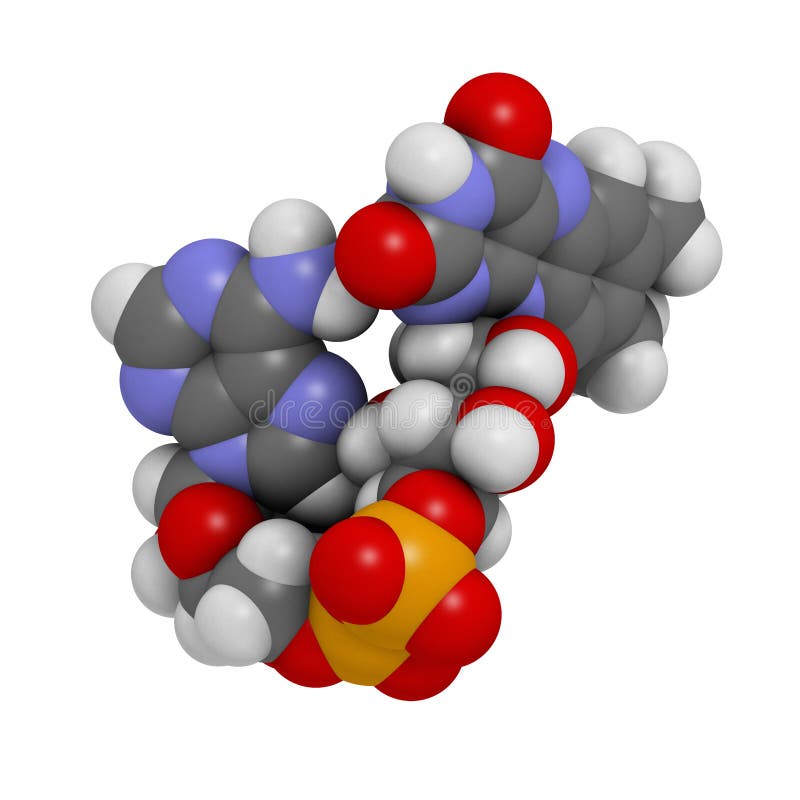
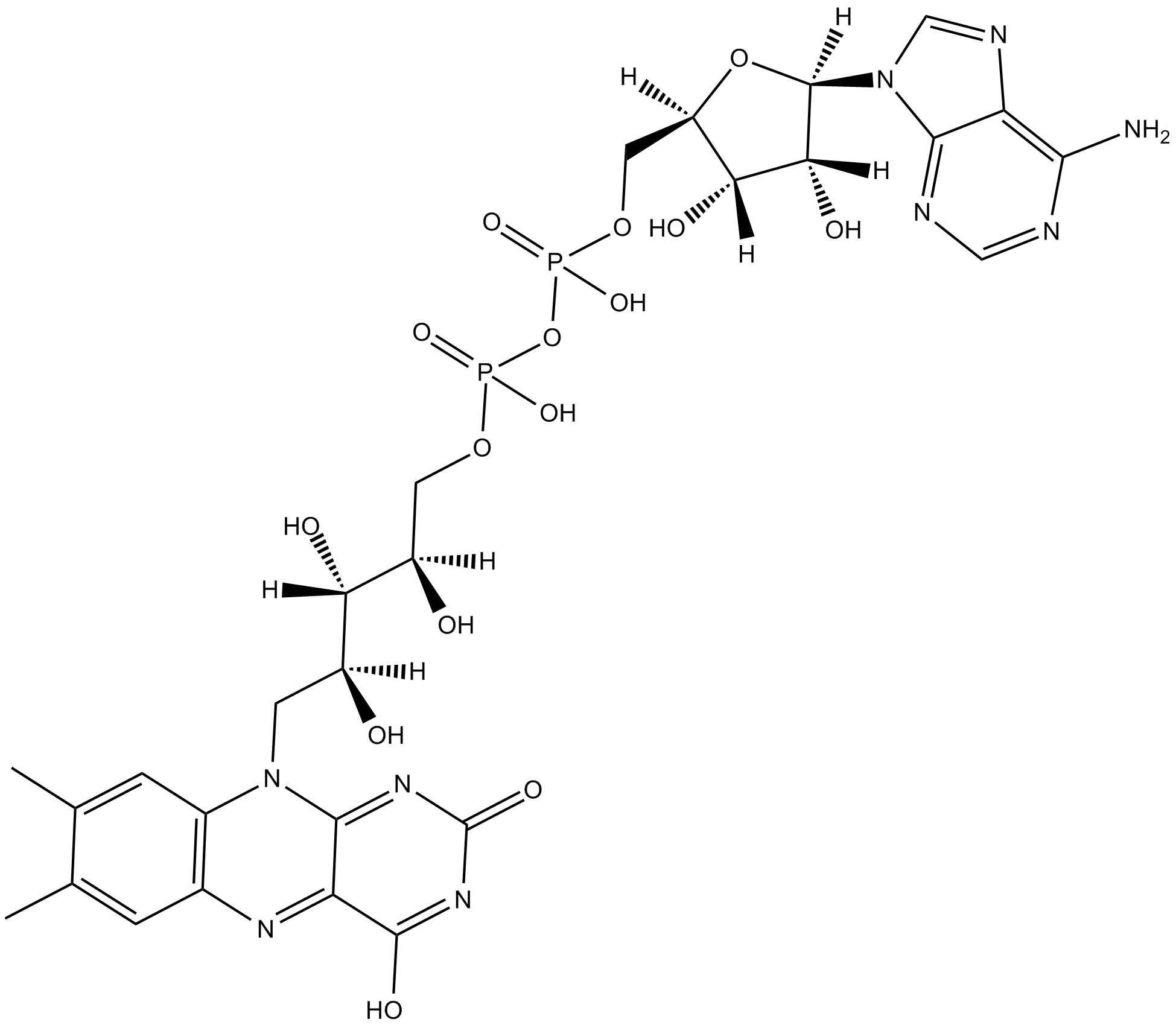
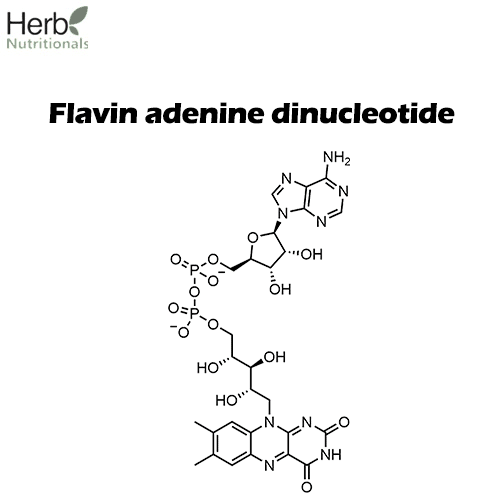
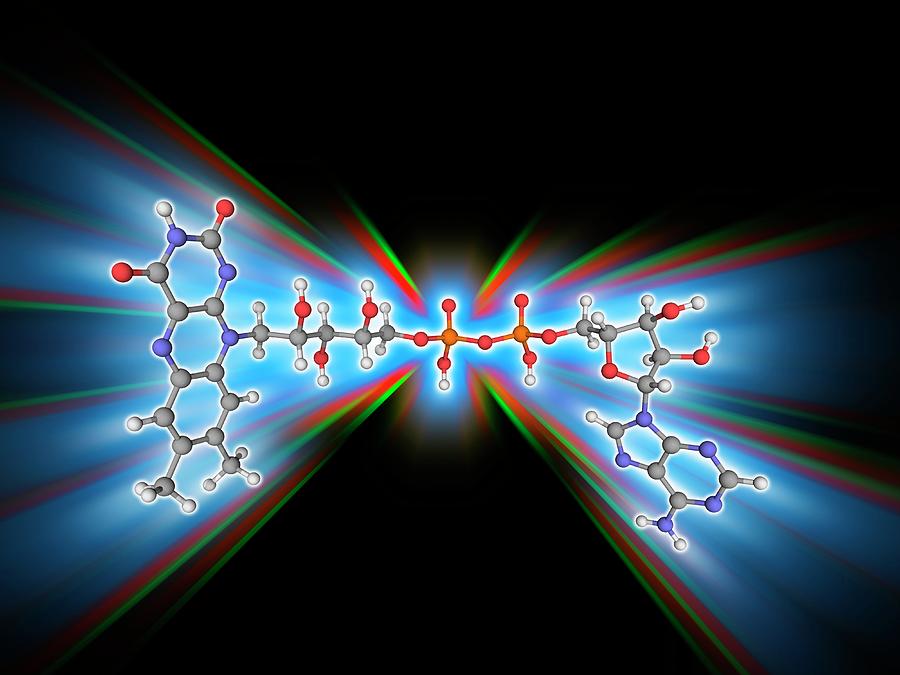
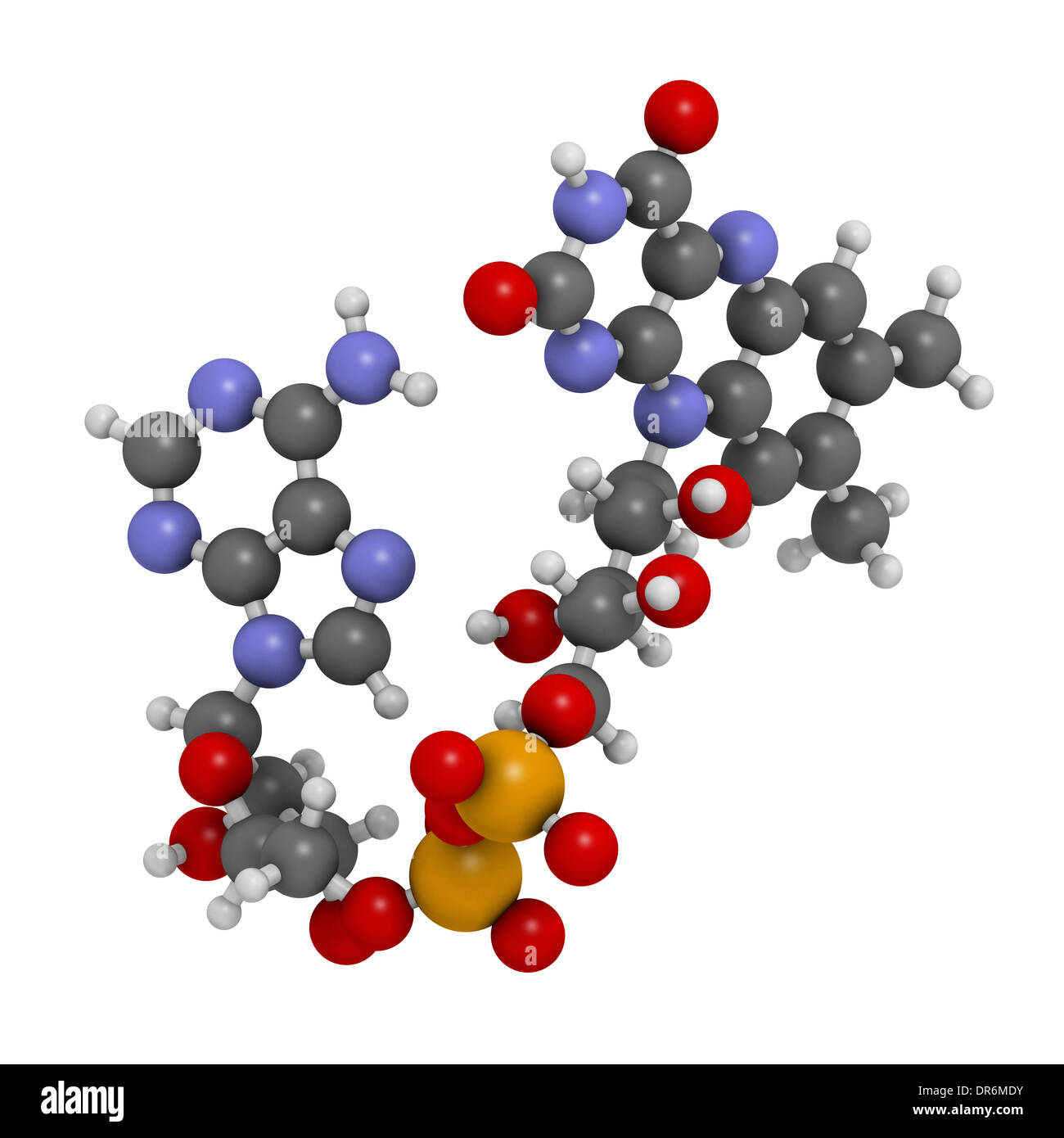
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Is A Coenzyme Form Of The Vitamin
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Is A Coenzyme Form Of The Vitamin - These coenzymes serve as hydrogen. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group , which may be in the form of fad or. Web the active forms of riboflavin, vitamin b 2, are the coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (fmn; Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme that is a condensation product of riboflavin phosphate and adenylic acid; Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( nad) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Web the meaning of flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of vitamin b2 used in clinical conditions associated with vitamin b2 deficiency.
Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn, 1) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad, 2 ), the biologically active forms of riboflavin (vitamin b 2, 3 ), play a lead role in a diverse array of biological. Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( nad) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme that is a condensation product of riboflavin phosphate and adenylic acid; Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. [3] found in all living cells, nad is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of vitamin b2 used in clinical conditions associated with vitamin b2 deficiency. As shown it is the. Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin Web the meaning of flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins.
Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin glycolysis is a process involving reactions that convert glucose to pyruvate. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin _____. Principal pathways and cycles.in one reaction, the coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) to form nadh and fadh, respectively. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of vitamin b2 used in clinical conditions associated with vitamin b2 deficiency. Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn, 1) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad, 2 ), the biologically active forms of riboflavin (vitamin b 2, 3 ), play a lead role in a diverse array of biological. Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme that is a condensation product of riboflavin phosphate and adenylic acid; As shown it is the. A coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins… see the full.
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Fad Redox Coenzyme Molecule. Skeletformule
Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin Principal pathways and cycles.in one reaction, the coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) to form nadh and fadh, respectively. As shown it is the. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme that is a condensation product of riboflavin phosphate and adenylic acid; Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( nad) is a coenzyme central to metabolism.
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Molecule Photograph by Laguna Design
As shown it is the. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin Although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer.
FileFlavin adenine dinucleotide.png Wikimedia Commons
Web the meaning of flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin glycolysis is a process involving reactions that convert glucose to pyruvate. Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon.
Flavin adenine dinucleotide FAD molecule Stock Image F004/8449
[3] found in all living cells, nad is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides. These coenzymes serve as hydrogen. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. A coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins… see the full. Figure 2) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad).
Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide FAD Redox Coenzyme Molecule. Skeletal
Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin glycolysis is a process involving reactions that convert glucose to pyruvate. Web riboflavin is the precursor of the coenzymes flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn). Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. Web.
APExBIO Flavin adenine dinucleotide CAS 146145
Web nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide ( nad) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. A coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins… see the full. Web the active forms of riboflavin, vitamin b 2, are the coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (fmn; [3] found in all living cells, nad is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides. Web although not used in the electron.
Flavin adenine dinucleotide,FAD,84366814
These coenzymes serve as hydrogen. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. Although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a.
Fad (flavin Adenine Dinucleotide) Molecule Photograph by Laguna Design
Principal pathways and cycles.in one reaction, the coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) to form nadh and fadh, respectively. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group , which may be in the form of fad or. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin riboflavin glycolysis is a process involving reactions that convert glucose to.
FlavinAdenine Dinucleotide; FAD
[3] found in all living cells, nad is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides. As shown it is the. Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin _____.
Flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) redox coenzyme molecule. Atoms are
Web the meaning of flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins. Although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to.
Web Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide (Fad) A Coenzyme That Is A Condensation Product Of Riboflavin Phosphate And Adenylic Acid;
Pantothenic acid niacin thiamin riboflavin A coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins… see the full. As shown it is the. Principal pathways and cycles.in one reaction, the coenzyme flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) to form nadh and fadh, respectively.
[3] Found In All Living Cells, Nad Is Called A Dinucleotide Because It Consists Of Two Nucleotides.
Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of vitamin b2 used in clinical conditions associated with vitamin b2 deficiency. Web flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme form of the vitamin _____. A flavoprotein is a protein that contains a flavin group , which may be in the form of fad or. Web flavin mononucleotide (fmn, 1) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad, 2 ), the biologically active forms of riboflavin (vitamin b 2, 3 ), play a lead role in a diverse array of biological.
Web Flavin Adenine Dinucleotide Is A Coenzyme Form Of The Vitamin Riboflavin Glycolysis Is A Process Involving Reactions That Convert Glucose To Pyruvate.
These coenzymes serve as hydrogen. Web the active forms of riboflavin, vitamin b 2, are the coenzymes flavin mononucleotide (fmn; Web riboflavin is the precursor of the coenzymes flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) and flavin mononucleotide (fmn). Although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl.
Web Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide ( Nad) Is A Coenzyme Central To Metabolism.
Web although not used in the electron transport chain, coenzyme a is a major cofactor which is used to transfer a two carbon unit commonly referred to as the acetyl group. Web the meaning of flavin adenine dinucleotide is a coenzyme c27h33n9o15p2 of some flavoproteins. Figure 2) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad). Web flavin adenine dinucleotide (fad) a coenzyme derivative of the vitamin riboflavin, which participates in dehydrogenation reactions mediated by flavoproteins.