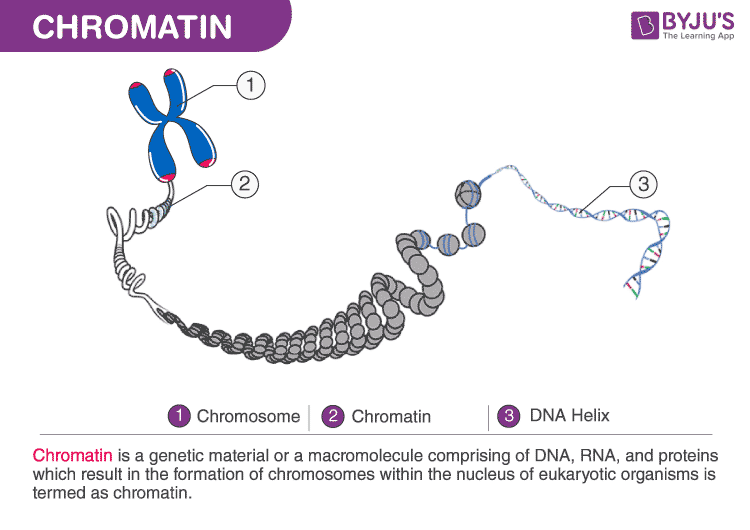
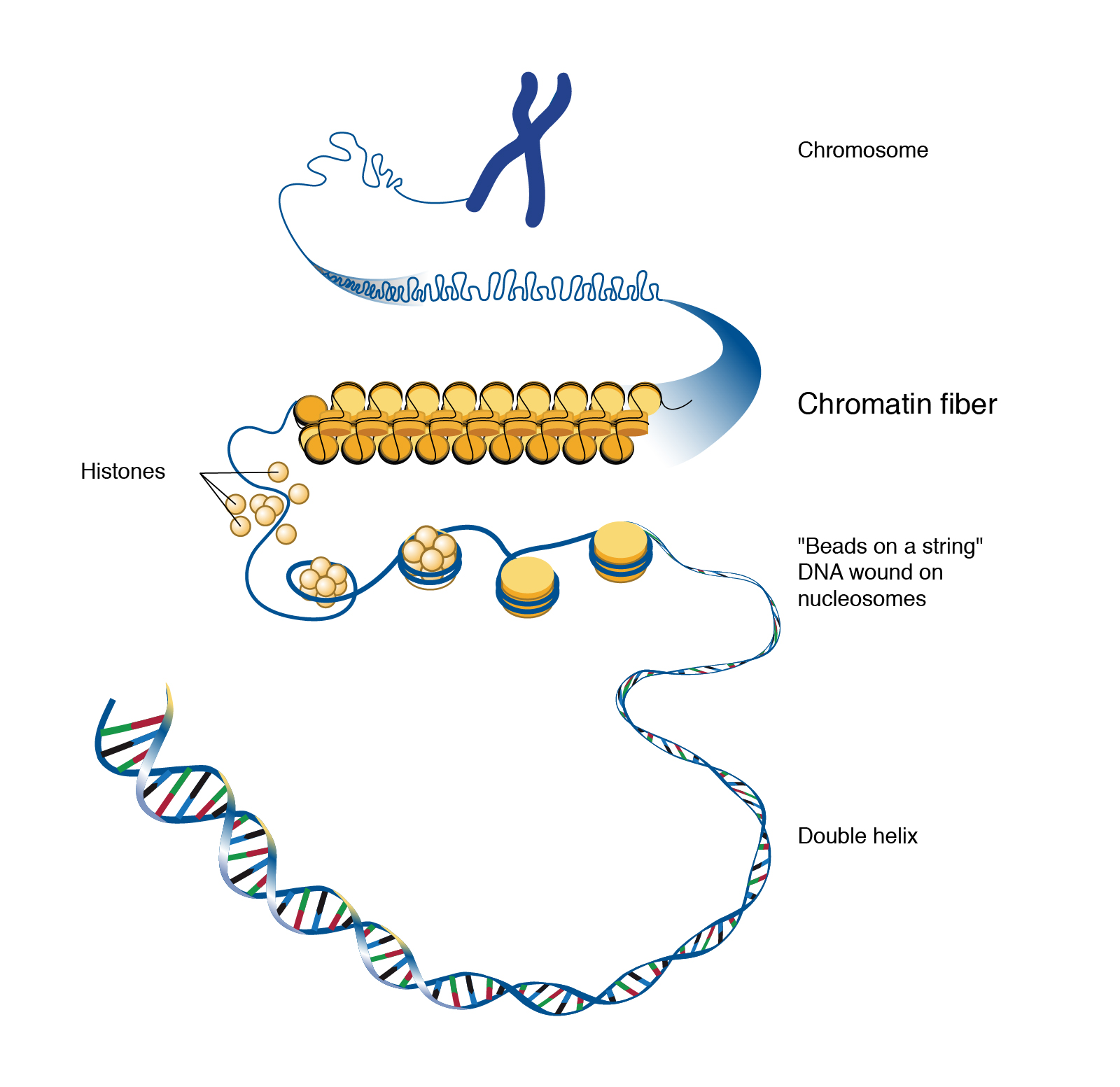
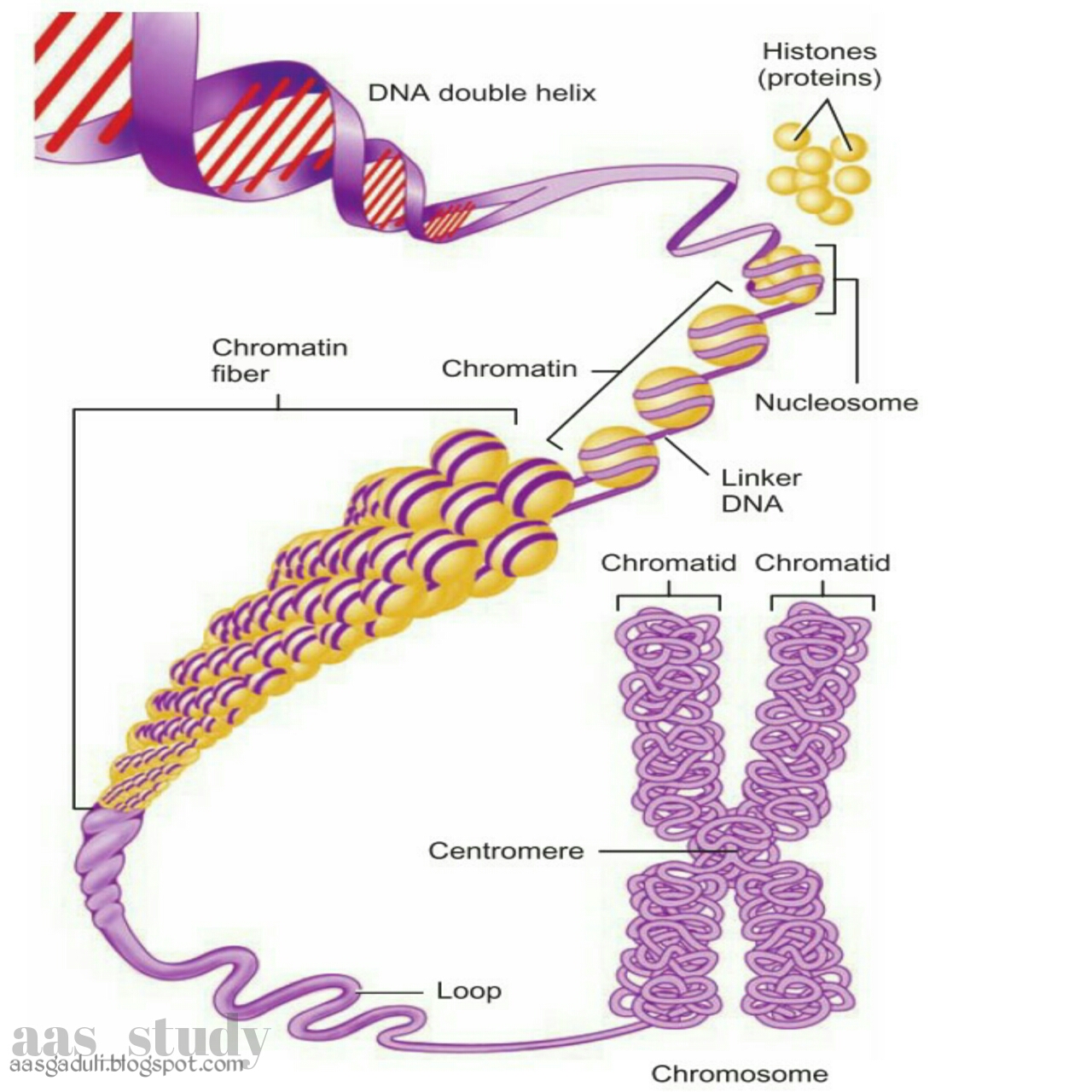
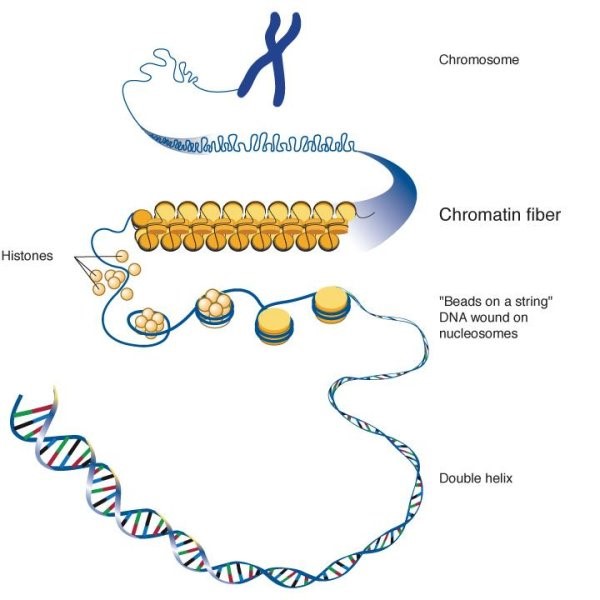
Chromatin Condenses To Form Chromosomes
Chromatin Condenses To Form Chromosomes - Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. Chromosomal structure is not inert. In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. Studies of the molecular mechanisms. During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the. Web the chromatin condenses and the cell gets ready to get separated into two cells. Web what stage does chromatin condense to chromosomes? Web although chromatin changes are already detectable before nuclear envelope breakdown, this leads to further chromatin condensation and allows assembly. Web chromatin condensation and dna fragmentation are hallmarks of apoptosis, and therefore, apoptotic signaling cascades must target chromatin to mediate these effects. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure. In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. Studies of the molecular mechanisms. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. Web chromatin condensation and dna fragmentation are hallmarks of apoptosis, and therefore, apoptotic signaling cascades must target chromatin to mediate these effects. Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; Web although chromatin changes are already detectable before nuclear envelope breakdown, this leads to further chromatin condensation and allows assembly. Web solution the correct option is a true chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure. I don't know it exactly, but i guess it is coming from before the microtubules attach. Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the. Web solution the correct option is a true chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Wolffe, in chromatin (third edition), 2000 2.5 modulation of chromosomal structure. Web what stage does chromatin condense to chromosomes? Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells.
Human Biology Online Lab / Chromatin By Kendall Setts
Web although chromatin changes are already detectable before nuclear envelope breakdown, this leads to further chromatin condensation and allows assembly. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. Web chromatin condensation and dna fragmentation are.
modifications of chromatin structure. Chromosomes are
During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the. Web solution the correct option is a true chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of.
Everything to Know about Chromatin In Plant Cell Garden Bagan
During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the. I don't know it exactly, but i guess it is coming from before the microtubules attach. Studies of the molecular mechanisms. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. Web the chromatin condenses and the cell gets ready to get.
chromatin und Gesundheit
Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. Web what stage does chromatin condense to chromosomes? During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different.
What is the phase where chromatin condenses to form chromosomes
Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; Chromosomal structure is not inert. Web what stage does chromatin condense to chromosomes? They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and.
Nucleus
The dna is thus condensed. Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. Chromosomal structure is not inert. Web the chromatin condenses and the cell gets ready to get separated into two cells. Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands;
chromosomes chromatin Google Search med Pinterest
The dna is thus condensed. Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure. Chromosomal structure is not.
The Structure and Function of Chromatin
Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. The dna is thus condensed. Chromosomal structure is not inert. Web solution the correct option is a true chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
Epigenomics approach illuminates the dark corners of the genome Broad
They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure. Web chromatin condensation and dna fragmentation are hallmarks of apoptosis, and therefore, apoptotic signaling cascades must target chromatin to mediate these effects. Studies of the molecular mechanisms. Web although chromatin changes are already detectable before nuclear envelope breakdown, this leads to further chromatin condensation and allows assembly. I.
Different Types of Chromosome Condensation (A) Mitotic chromosome
Web solution the correct option is a true chromatin condenses to form chromosomes during cell division. I don't know it exactly, but i guess it is coming from before the microtubules attach. Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the..
Wolffe, In Chromatin (Third Edition), 2000 2.5 Modulation Of Chromosomal Structure.
Web chromatin is a complex of dna and proteins that forms chromosomes within the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. Nuclear dna does not appear in free linear strands; I don't know it exactly, but i guess it is coming from before the microtubules attach. Web chromatin condensation and dna fragmentation are hallmarks of apoptosis, and therefore, apoptotic signaling cascades must target chromatin to mediate these effects.
Web The Chromatin Condenses And The Cell Gets Ready To Get Separated Into Two Cells.
Chromatin condensation changes during the cell cycle. In the past decade, two major advances in our understanding of nuclear organization have taken the field of gene regulation by. The dna is thus condensed. During interphase (1), chromatin is in its least condensed state and appears loosely distributed throughout the.
Web Solution The Correct Option Is A True Chromatin Condenses To Form Chromosomes During Cell Division.
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes during prophase, the first phase of mitosis, and. Chromosomal structure is not inert. Web although chromatin changes are already detectable before nuclear envelope breakdown, this leads to further chromatin condensation and allows assembly. They are both essentially the same thing, but with a different structure.
Studies Of The Molecular Mechanisms.
Web what stage does chromatin condense to chromosomes?