Chapter 6 The Periodic Table And Periodic Law
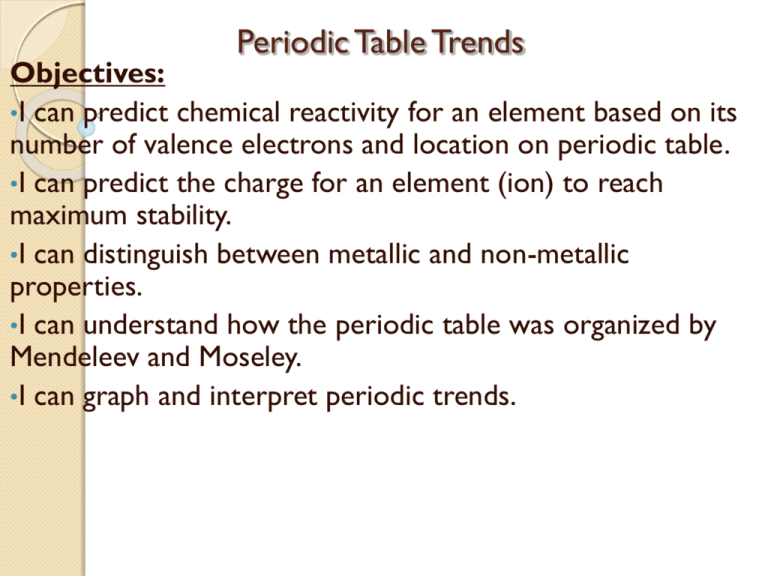
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table And Periodic Law - Identify different key features of the periodic table. He discovered that the properties of elements repeat in a periodic way. Group 1 a elements, except for hydrogen, that are on the left side of the modern periodic. The law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements. The periodic table and periodic law in this chapter: Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6, the periodic table and periodic law, glencoe chemistry by numerade The periodic table and periodic law. Include contributions made by lavoisier, newlands, mendeleev, and moseley. Web problem 1 describe the development of the modern periodic table. Web increasing atomic number is called the periodic law.
Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6, the periodic table and periodic law, glencoe chemistry by numerade Web the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. The periodic table and periodic law in this chapter: He discovered that the properties of elements repeat in a periodic way. Click the card to flip 👆. The periodic table and periodic law. That when elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. Web start studying chapter 6: Web tjdubinski terms in this set (26) periodic law states that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their properties. The arrangement of the periodic table is based on the number of:
Group 1 a elements, except for hydrogen, that are on the left side of the modern periodic. The periodic table and periodic law. Web periodic law (6.1) statement that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements when arranged by increasing atomic number. The periodic table and periodic law in this chapter: What did newlands discovered (1865)? Protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. Include contributions made by lavoisier, newlands, mendeleev, and moseley. Group a vertical column of elements in the periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number;. Click the card to flip 👆. Reading check compare and contrast the ways in which mendeleev and moseley organized the elements.
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
Web problem 1 describe the development of the modern periodic table. Protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. A column on the periodic table. Web 1/16 previous ← next → flip space created by ambssbabyy123 chemistry test review terms in this set (16) periodic law statement that when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, there.
Chapter 6 Periodic table
That when elements are arranged according to increasing atomic number there is a periodic repetition of their chemical and physical properties. Lilia pronin numerade educator 01:12 problem 2 sketch a simplified. Web increasing atomic number is called the periodic law. Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6, the periodic table and periodic law, glencoe chemistry by numerade.
Chapter 6 Periodic Table CeilidhMavi
Web increasing atomic number is called the periodic law. Protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. Web periodic law (6.1) statement that there is a periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of the elements when arranged by increasing atomic number. Web problem 1 describe the development of the modern periodic table. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more.
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table And Periodic Law Study Guide Study Poster
Group a vertical column of elements in the periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number;. Representative elements group a elements transition elements group b elements Relate the group and period trends seen in. The law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements. Web the number.
Chemistry Chapter 6 The Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
Properties of groups and periods in the late 1800s, russian chemist dmitri mendeleev created the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic weight in increasing. Representative elements group a elements transition elements group b elements Protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. The periodic table and periodic law. A column on the periodic table.
Chapter 6 Study Guide The Periodic Table And Periodic Law Study Poster
Include contributions made by lavoisier, newlands, mendeleev, and moseley. Group 1 a elements, except for hydrogen, that are on the left side of the modern periodic. When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties. Table 6.2 summarizes the contributions of. A column on the periodic table.
Chapter 6 the periodic table
Click the card to flip 👆. Group a vertical column of elements in the periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number;. Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6, the periodic table and periodic law, glencoe chemistry by numerade Protons in the nucleus of an atom of the element. Web the number of protons in the.
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The periodic table and periodic law. When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties. Web the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter.
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
Click the card to flip 👆. Web increasing atomic number is called the periodic law. A column on the periodic table. Representative elements group a elements transition elements group b elements Web 1/16 previous ← next → flip space created by ambssbabyy123 chemistry test review terms in this set (16) periodic law statement that when the elements are arranged by.
Chemistry Chapter 6 The Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
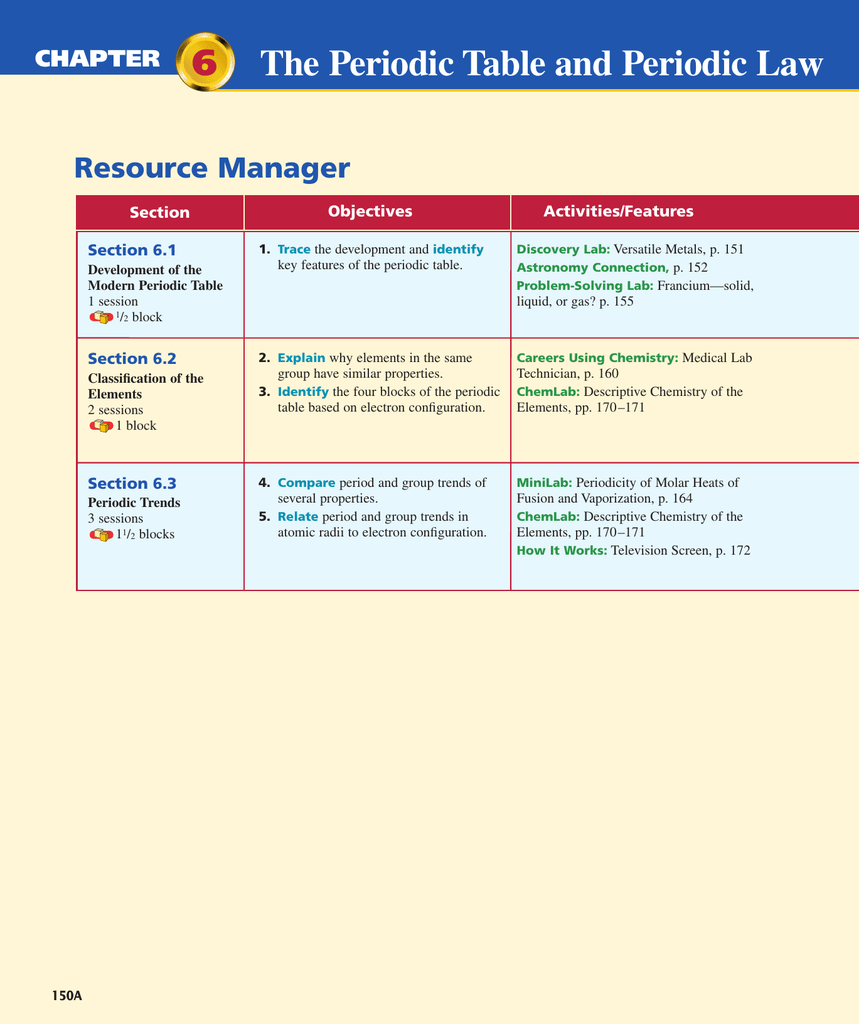
The law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements. Relate the group and period trends seen in. Web chapter 6 the periodic table and periodic law section 6.1 development of the pt 1. The periodic table and periodic law. What did newlands discovered (1865)?
The Arrangement Of The Periodic Table Is Based On The Number Of:
Lilia pronin numerade educator 01:12 problem 2 sketch a simplified. Reading check compare and contrast the ways in which mendeleev and moseley organized the elements. Properties of groups and periods in the late 1800s, russian chemist dmitri mendeleev created the periodic table by organizing elements by their atomic weight in increasing. Group 1 a elements, except for hydrogen, that are on the left side of the modern periodic.
What Did Newlands Discovered (1865)?
When interpreted properly, the table describes much of the elements physical. The law that states that the repeating chemical and physical properties of elements change periodically with the atomic numbers of the elements. Identify different key features of the periodic table. Table 6.2 summarizes the contributions of.
That When Elements Are Arranged According To Increasing Atomic Number There Is A Periodic Repetition Of Their Chemical And Physical Properties.
Click the card to flip 👆. He discovered that the properties of elements repeat in a periodic way. A column on the periodic table. When the elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic pattern in their physical and chemical properties.
Protons In The Nucleus Of An Atom Of The Element.
Web video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 6, the periodic table and periodic law, glencoe chemistry by numerade Group a vertical column of elements in the periodic table arranged in order of increasing atomic number;. Web problem 1 describe the development of the modern periodic table. Explain why elements in a group have similar properties.