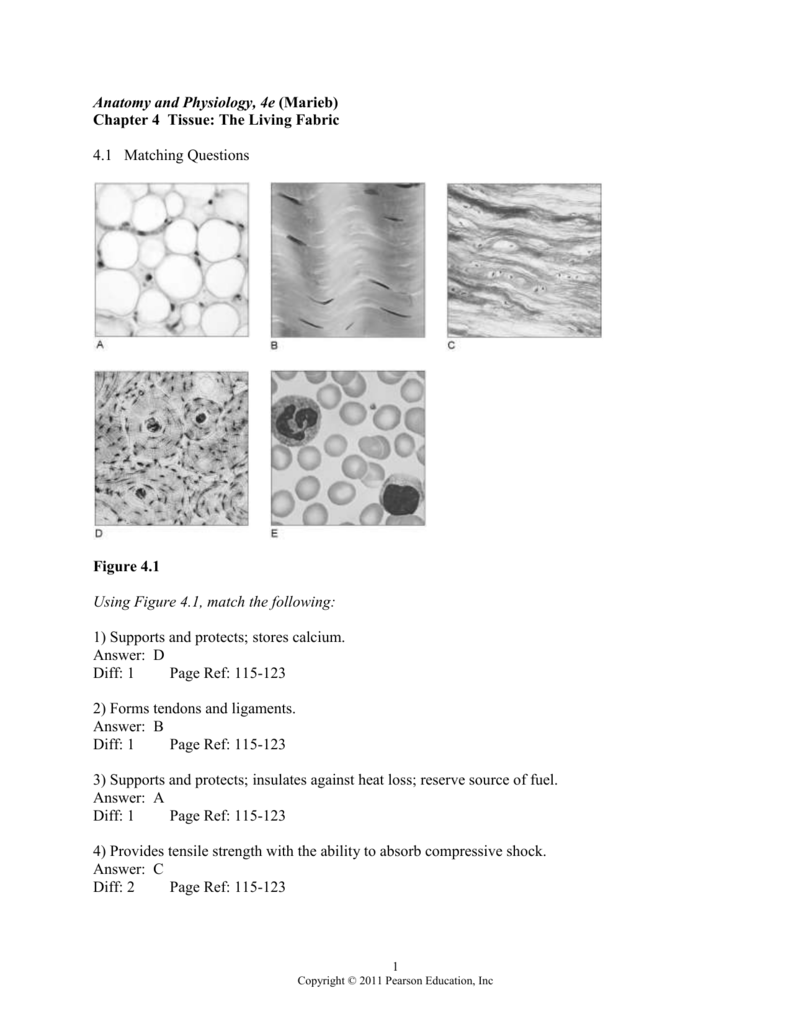
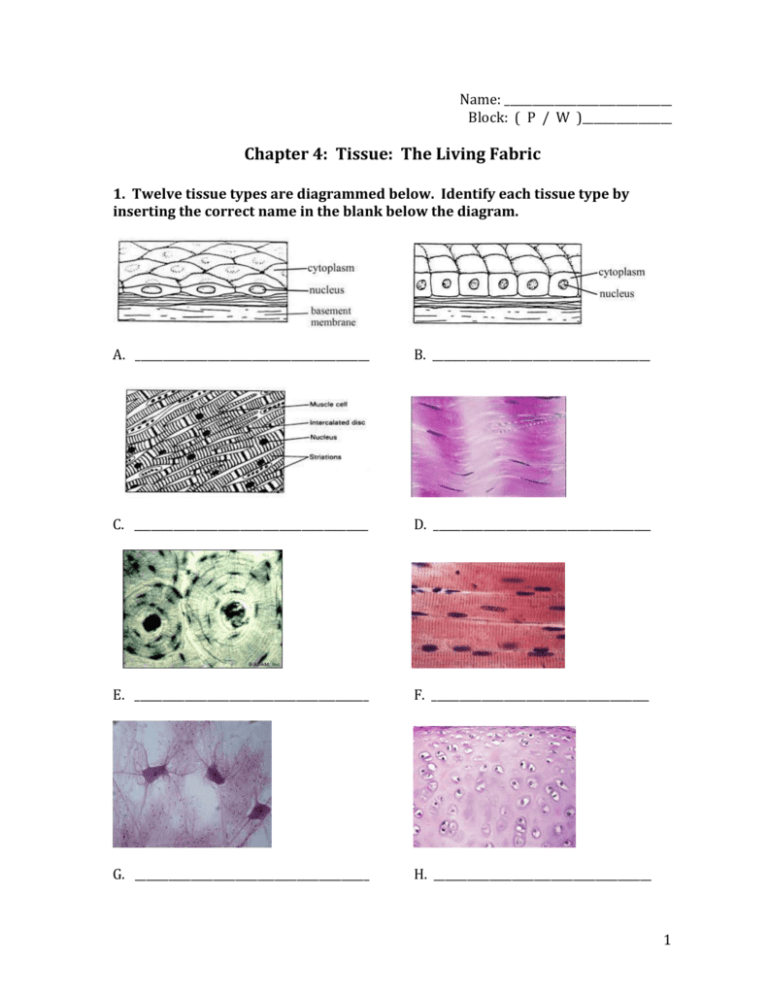
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric - Rizona_ terms in this set (64) tissues. Any tissues that exist in layers and form linings or coverings fall into the category of stratified epithelia. Ch 6, 7 and 8: Web biology histology chapter 4: Epithelial (covering) connective (support) muscle (movement) nervous (control) epithelial tissue. The middle portion of unspecialized mesoderm from which cartilage, bone, and blood develop is called mesenchyme. Tissues types of connective tissue: There are four basic types of tissue are present in the human body these includes epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. A group of cells similar in structure; Matrix (most of volume) cell fibers protein 3) ground substance (fluid) 2) protein fibers (extracellular) b) fiber types:
At first glance, it appears that they tissue has multiple cell layers, but upon closer investigation you see that all of the. B) the clot is formed from dried blood and transposed collagen fibers. Collagen fibers, and collagen sheets. There are four basic types of tissue are present in the human body these includes epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissue. C) granulation tissue is another name for a blood clot. Web human anatomy and physiology, chapter 4: The integumentary system lecture notes. Location & type of fibers of reticular connective tissue. Any tissues that exist in layers and form linings or coverings fall into the category of stratified epithelia. Web regenerative germinative cells (stem cells) chapter 4:
Web human anatomy and physiology, chapter 4: •understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. Epithelial (covering) connective (support) muscle (movement) nervous (control) epithelial tissue. Web 4 primary tissues in the body. To make the specimen thin enough to transmit light or electrons to avoid microscopy artifacts to. Web biology histology chapter 4: Ch 6, 7 and 8: You observe a tissue that has cells of varying heights. Rizona_ terms in this set (64) tissues. Under the skin under the subcutaneous tissue, eyeball, abdomen, and in breasts.
Chapter 4 * Tissue The Living Fabric
The living fabric tissues introduction tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and. •understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. Collagen fibers, and collagen sheets. The living fabric (chapter practice test) why are histological sections stained? 1.9k views 2 years ago bsc2085 (ap1)_ video recordings.
Human Anatomy and Physiology, Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric
Web ch 3, 4 and 5: C) granulation tissue is another name for a blood clot. •understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. Web biology histology chapter 4: Rizona_ terms in this set (64) tissues.
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Answers MyleyLayseigh
Web 4 primary tissues in the body. B) the clot is formed from dried blood and transposed collagen fibers. Web human anatomy and physiology, chapter 4: The living fabric define the term histology versus cytology. Under the skin under the subcutaneous tissue, eyeball, abdomen, and in breasts.
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Answers MyleyLayseigh
You observe a tissue that has cells of varying heights. 1.9k views 2 years ago bsc2085 (ap1)_ video recordings. Tissues types of connective tissue: C) granulation tissue is another name for a blood clot. To make the specimen thin enough to transmit light or electrons to avoid microscopy artifacts to.
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Study Guide Answer Key Study Poster
Location & type of fibers of reticular connective tissue. Designed to perform a specialized function primary tissue types: Web 4 primary tissues in the body. Collagen fibers, and collagen sheets. The integumentary system lecture notes.
PPT Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric PowerPoint Presentation
The living fabric (chapter practice test) why are histological sections stained? Web a) granulation tissue is highly susceptible to infection. The middle portion of unspecialized mesoderm from which cartilage, bone, and blood develop is called mesenchyme. •understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. Rizona_ terms in this set (64) tissues.
Chapter 4 Homework Packet
The living fabric (chapter practice test) why are histological sections stained? The living fabric tissues introduction tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and. B) the clot is formed from dried blood and transposed collagen fibers. Web regenerative germinative cells (stem cells) chapter 4: The living fabric lecture notes.
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Epithelium Cartilage
Ch 6, 7 and 8: Under the skin under the subcutaneous tissue, eyeball, abdomen, and in breasts. Designed to perform a specialized function primary tissue types: Web ch 3, 4 and 5: Web a) granulation tissue is highly susceptible to infection.
Chapter 4 Tissue The Living Fabric Study Guide Answer Key Study Poster
At first glance, it appears that they tissue has multiple cell layers, but upon closer investigation you see that all of the. Matrix (most of volume) cell fibers protein 3) ground substance (fluid) 2) protein fibers (extracellular) b) fiber types: The middle portion of unspecialized mesoderm from which cartilage, bone, and blood develop is called mesenchyme. Under the skin under.
Tissue The Living Fabric
At first glance, it appears that they tissue has multiple cell layers, but upon closer investigation you see that all of the. B) the clot is formed from dried blood and transposed collagen fibers. Tissues types of connective tissue: •understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. There are four basic types.
The Living Fabric Lecture Notes.
Web biology histology chapter 4: Web human anatomy and physiology, chapter 4: The middle portion of unspecialized mesoderm from which cartilage, bone, and blood develop is called mesenchyme. The living fabric define the term histology versus cytology.
Tissue That Covers Outside Of The Body And Lines Organs And Cavities.
The living fabric tissues introduction tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and. The living units lecture notes. Any tissues that exist in layers and form linings or coverings fall into the category of stratified epithelia. A group of cells similar in structure;
Tissues Types Of Connective Tissue:
Epithelial (covering) connective (support) muscle (movement) nervous (control) epithelial tissue. B) the clot is formed from dried blood and transposed collagen fibers. Web a) granulation tissue is highly susceptible to infection. Collagen fibers, and collagen sheets.
The Living Fabric (Chapter Practice Test) Why Are Histological Sections Stained?
•understanding types of tissues allows you to monitor potential tissue damage, such as bedsores, in patients. Under the skin under the subcutaneous tissue, eyeball, abdomen, and in breasts. Ch 6, 7 and 8: You observe a tissue that has cells of varying heights.