Bash Read Array From File
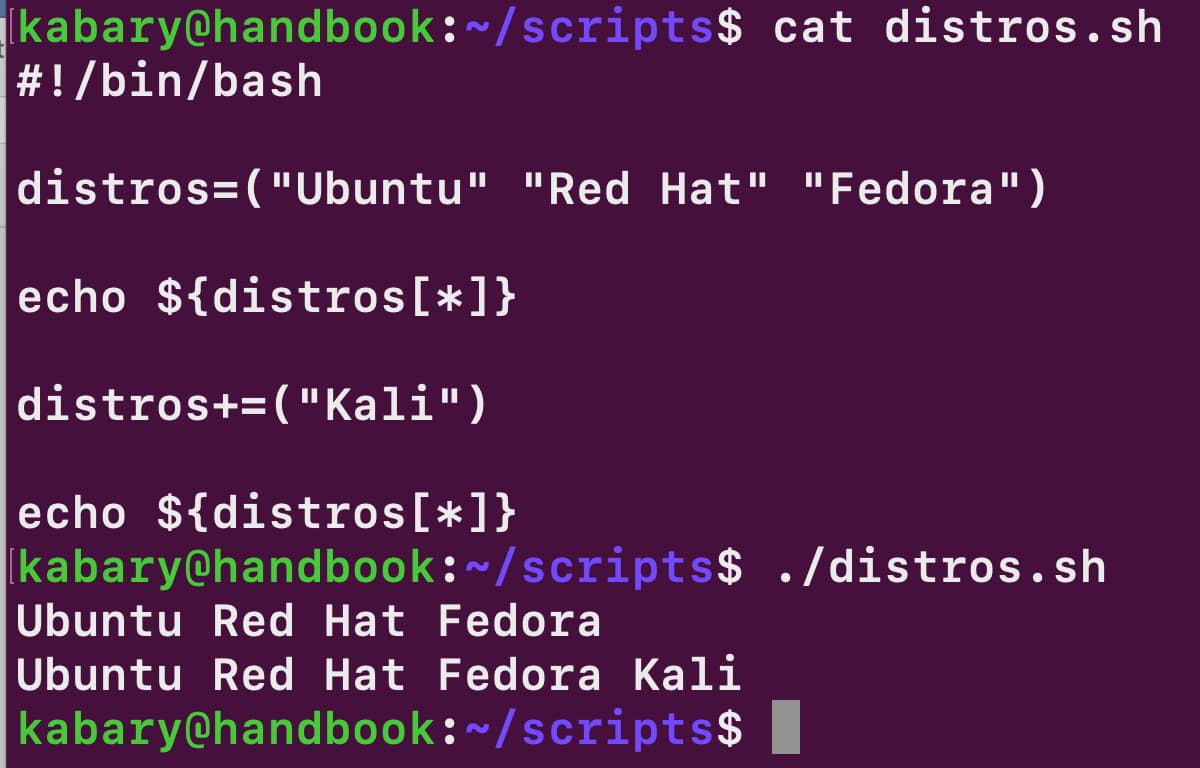
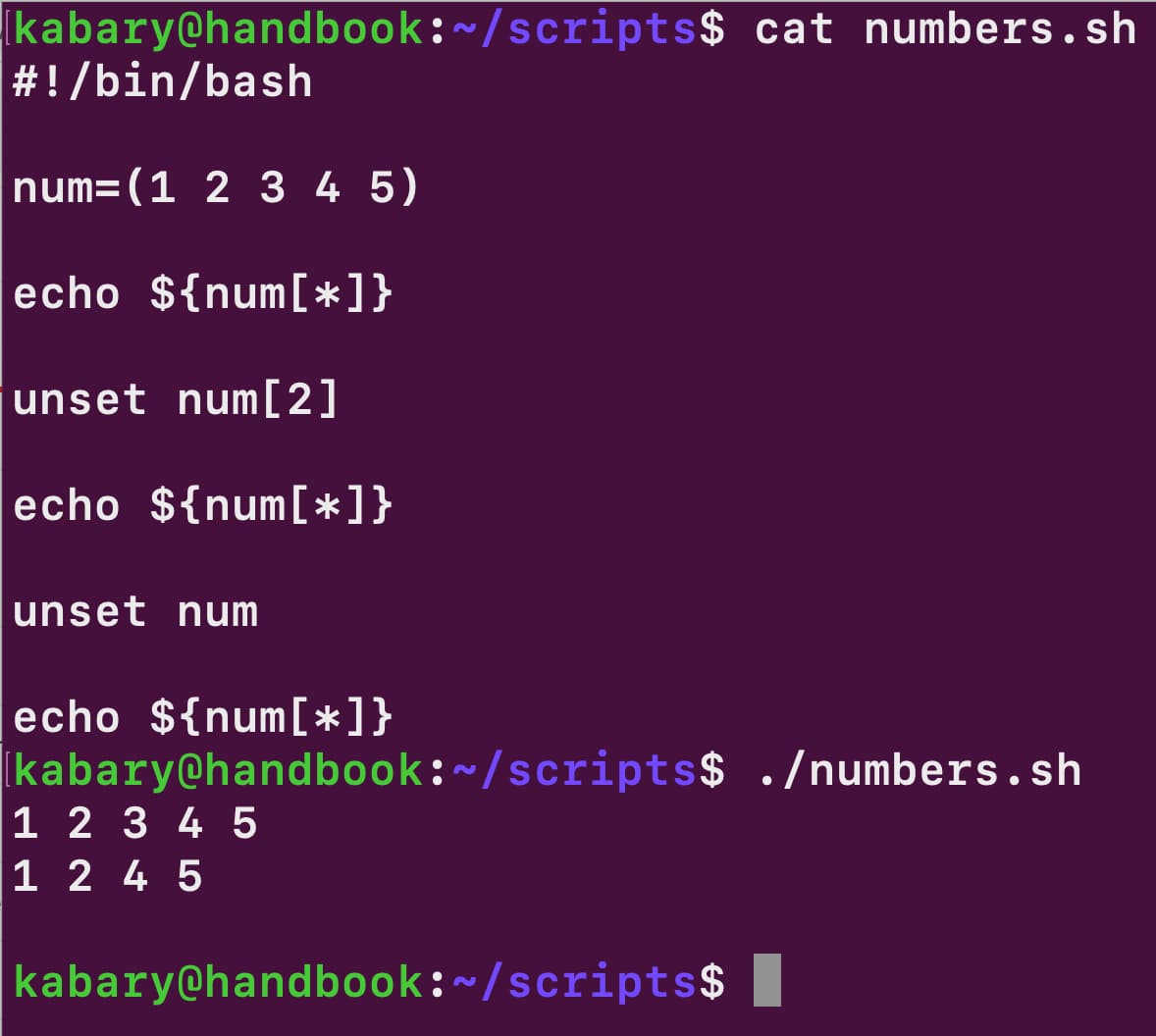
Bash Read Array From File - Web bash readarray from bash version 4, storing the contents in an array has become straightforward. #!/bin/bash files= (f1.txt f2.txt f3.txt f4.txt f5.txt) echo $ {files [4]} echo $ {files [3]} echo $ {files [2]} echo $ {files [1]} echo $ {files. There may be cases where we prefer to map the entire csv file into an array. Type a sentence and press enter. Do arr+= ($line) done <<strong>file</strong> got any bash. The readarray utility simply read lines from the standard input into the indexed array. Web using read or mapfile, we can declare and populate a bash array in one go. Web in a question titled bash reading txt file and storing in array i feel readarray deserves a mention. (the ifs value determines the delimiter, which is whitespace by default.) the array. Write the command and press enter:
Web 1 answer sorted by: An example of this method i use to read test files into an array would be: Echo $reply the $reply variable stores the read. Web 19 i'm trying to search for files using find, and put those files into a bash array so that i can do other operations on them (e.g. Web the following bash script reverse.sh would print out all the five values in your files array in reversed order, starting with the last array element: Web readarray will create an array where each element of the array is a line in the input. The terminal returns to its normal state. Do arr+= ($line) done <<strong>file</strong> got any bash. Parsing csv file into a bash array. Write the command and press enter:
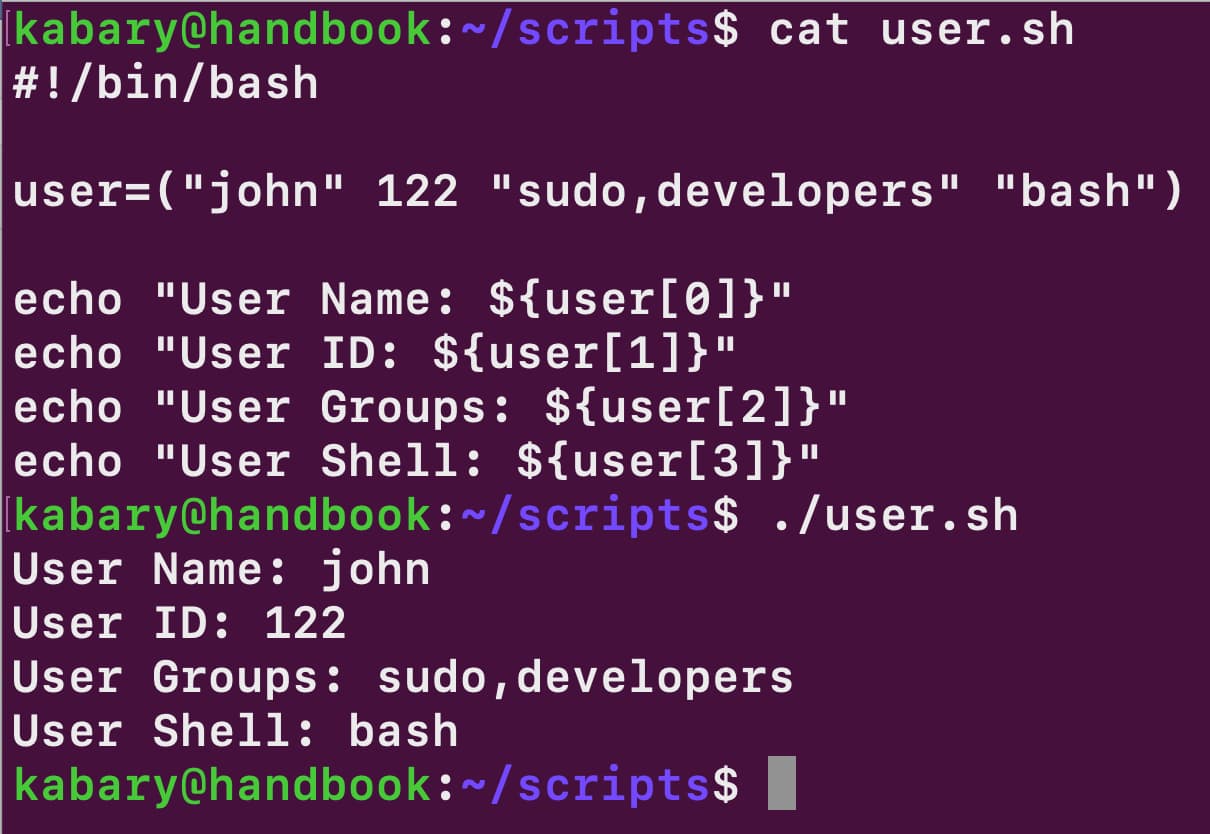
Read the prompt waits for the user input. If you want to see the whole array you need to use. Instead of using multiple variables, you can use arrays in bash to store values in the same category. The readarray utility simply read lines from the standard input into the indexed array. Parsing csv file into a bash array. It can also be read from the file. Do arr+=($line) done < file in case the file has an incomplete (missing newline) last line, you could use. #!/bin/bash files= (f1.txt f2.txt f3.txt f4.txt f5.txt) echo $ {files [4]} echo $ {files [3]} echo $ {files [2]} echo $ {files [1]} echo $ {files. Web the <(.) section enables us to specify the tail command and lets bash read from its output like a file: Web the following bash script reverse.sh would print out all the five values in your files array in reversed order, starting with the last array element:
How To Store Values In An Array Using BASH Shell Script Siytek
${array_name[n]} like most other programming languages, the array. Say i have two files. Web 19 i'm trying to search for files using find, and put those files into a bash array so that i can do other operations on them (e.g. Web if you have an older version of bash, you can use a loop to read the file into.
How to Use Arrays in Bash Shell Scripts
Web readarray will create an array where each element of the array is a line in the input. It can also be read from the file. Retrieve the message with the echo command: (the ifs value determines the delimiter, which is whitespace by default.) the array. Write the command and press enter:
Full Guide to Bash Arrays
${array_name[n]} like most other programming languages, the array. Say i have two files. It can also be read from the file. Web 1 answer sorted by: Type a sentence and press enter.
Full Guide to Bash Arrays
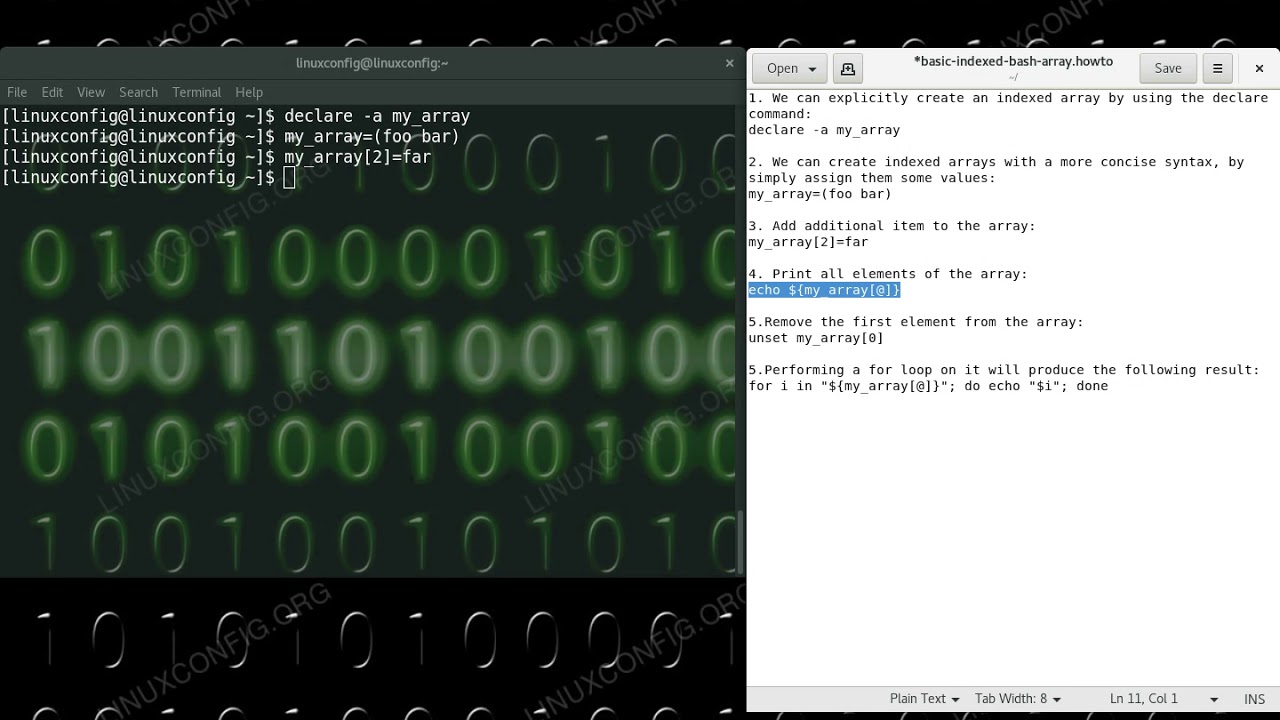
Web the <(.) section enables us to specify the tail command and lets bash read from its output like a file: Overview when we write shell scripts, we often call a command and save the output into a variable for further processing. Echo $reply the $reply variable stores the read. Echo ${myarray[@]} as echo $myarray will only output myarray[0], and..
How to Use Arrays in Bash Shell Scripts
The terminal returns to its normal state. Retrieve the message with the echo command: ${array_name[n]} like most other programming languages, the array. (the ifs value determines the delimiter, which is whitespace by default.) the array. Overview when we write shell scripts, we often call a command and save the output into a variable for further processing.
BASH SCRIPTING TUTORIAL 6 CREATING AN ARRAY YouTube
The readarray utility simply read lines from the standard input into the indexed array. Web in a question titled bash reading txt file and storing in array i feel readarray deserves a mention. There may be cases where we prefer to map the entire csv file into an array. Retrieve the message with the echo command: Instead of using multiple.
How to Use Arrays in Bash Shell Scripts
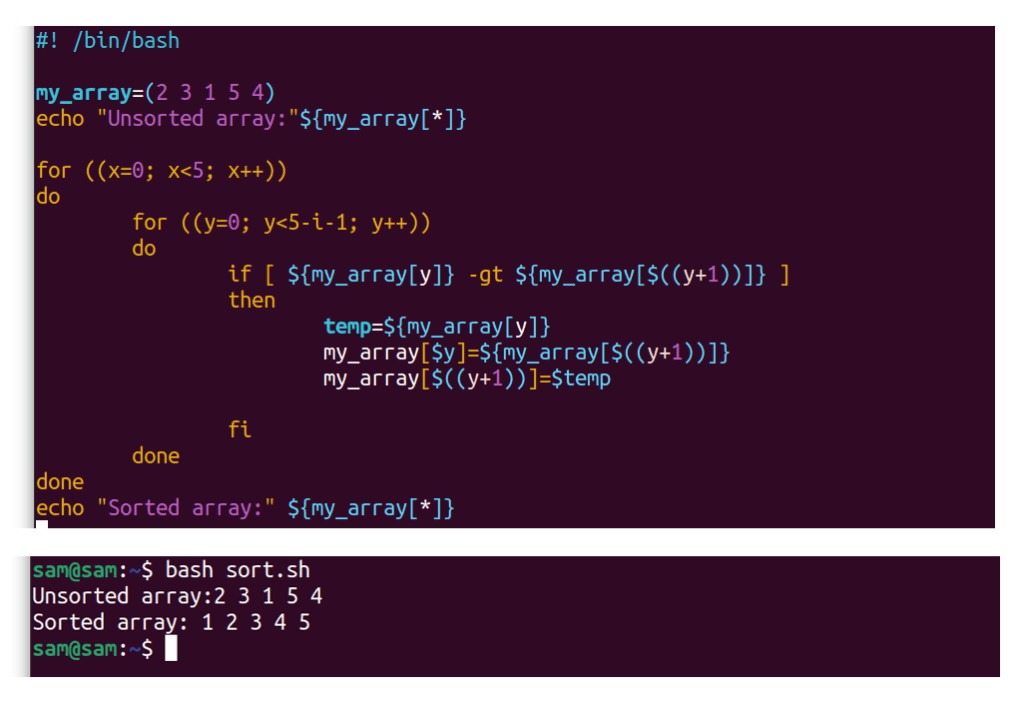
There may be cases where we prefer to map the entire csv file into an array. #!/bin/bash files= (f1.txt f2.txt f3.txt f4.txt f5.txt) echo $ {files [4]} echo $ {files [3]} echo $ {files [2]} echo $ {files [1]} echo $ {files. Prompt$ echo ${#arr[@]} 5 prompt$ echo ${arr[@]:0} a bc d e f prompt$ echo ${arr[2]} d prompt$ echo.
Bash Basics How to use read command on Linux YouTube
Web bash readarray from bash version 4, storing the contents in an array has become straightforward. The most reliable way to get a list of files is with a shell wildcard: Distros=(ubuntu fedora suse arch linux nix) to access an element, use: Read the prompt waits for the user input. Echo ${myarray[@]} as echo $myarray will only output myarray[0], and.
Creating basic indexed Bash array YouTube
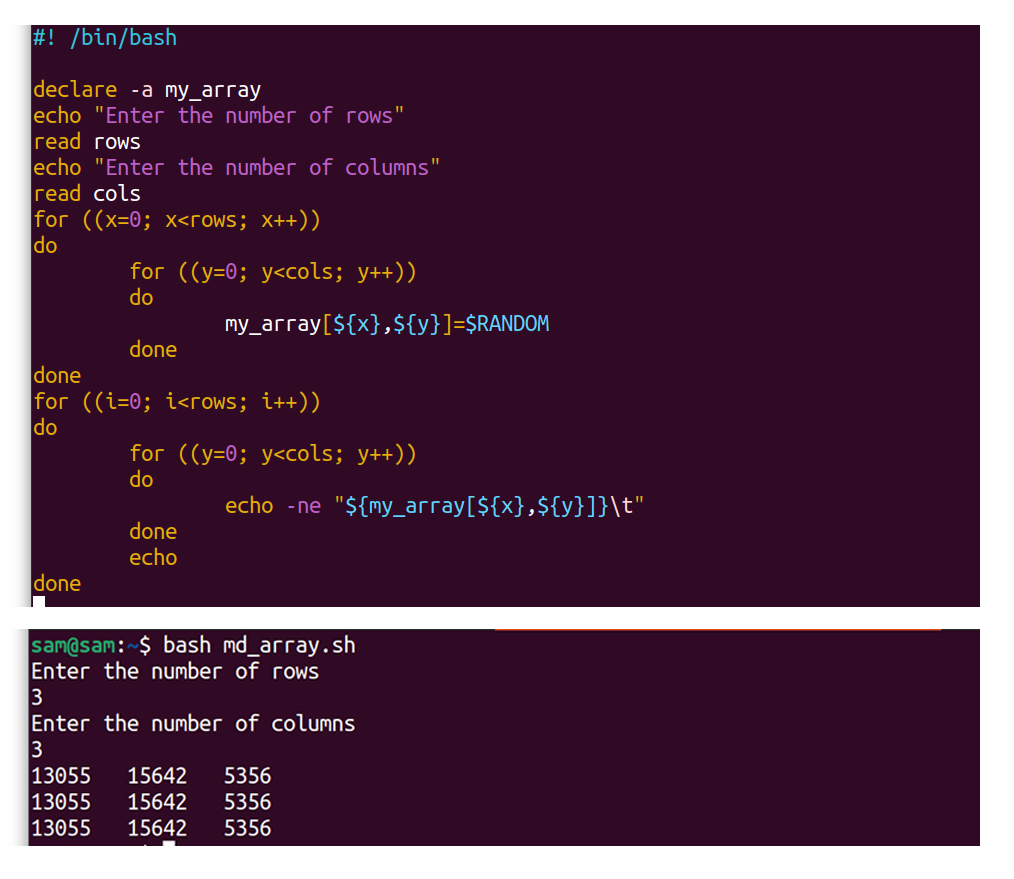
You can declare an array like this: Distros=(ubuntu fedora suse arch linux nix) to access an element, use: Web using read or mapfile, we can declare and populate a bash array in one go. Web if you have an older version of bash, you can use a loop to read the file into an array: We can then use the.
An Example Of This Method I Use To Read Test Files Into An Array Would Be:
Parsing csv file into a bash array. Web readarray will create an array where each element of the array is a line in the input. Write the command and press enter: Type a sentence and press enter.
Web The Following Bash Script Reverse.sh Would Print Out All The Five Values In Your Files Array In Reversed Order, Starting With The Last Array Element:
Web if you have an older version of bash, you can use a loop to read the file into an array: Web bash readarray from bash version 4, storing the contents in an array has become straightforward. We can then use the array. Do arr+= ($line) done <file got any bash.
Distros=(Ubuntu Fedora Suse Arch Linux Nix) To Access An Element, Use:
Prompt$ echo ${#arr[@]} 5 prompt$ echo ${arr[@]:0} a bc d e f prompt$ echo ${arr[2]} d prompt$ echo ${arr[3]} e i'm using the default ifs setting: The terminal returns to its normal state. Echo ${myarray[@]} as echo $myarray will only output myarray[0], and. #!/bin/bash files= (f1.txt f2.txt f3.txt f4.txt f5.txt) echo $ {files [4]} echo $ {files [3]} echo $ {files [2]} echo $ {files [1]} echo $ {files.
(The Ifs Value Determines The Delimiter, Which Is Whitespace By Default.) The Array.
${array_name[n]} like most other programming languages, the array. Using arrays in bash scripts. Echo $reply the $reply variable stores the read. Now you can easily read contents into the array.