Amino Acids Form Long Chains Called
Amino Acids Form Long Chains Called - Web amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups, i.e. Web amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein. Higher levels of protein structure are described in figure below. Linked together in long chains called polypeptides, amino acids are the building blocks for the vast assortment of proteins found in all living cells. At one end, the polypeptide has a free amino group, and this end is called the amino terminus (or. Polypeptides which have a molecular mass of 10,000 da or more are called proteins. Web proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Their other properties varying for each particular amino acid. Web protein structure when amino acids bind together, they may form short chains of two or just a few amino acids.
Web when amino acids bind together, they form a long chain called a polypeptide. Proteins are formed when these polypeptides not only connect, but elaborate into frankly really elegant structures. Peptide bonds are formed by a biochemical reaction that extracts a water molecule. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the. Peptide bond between amino acids. The lowest level, a protein’s primary structure, is its sequence of amino acids. Web what are long chains of amino acids called? The process of linking amino acids into proteins begins in the cell nucleus. A longer chain of linked amino acids (51 or more) is a polypeptide. Web amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side chain.
Web peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Web amino acids form long chains called polypeptides. Web there are about 20 amino acids and they link together in molecular chains called polypeptides, which are the building blocks of proteins. Web protein structure when amino acids bind together, they may form short chains of two or just a few amino acids. Web amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups, i.e. Peptide bond between amino acids. Production of protein from amino acids. Web amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. Web the amino acid sequence produced by ribosomes can be written using different abbreviations.
Solved proteins are long chains of amino acids joined
At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the. Linked together in long chains called polypeptides, amino acids are the building blocks for the vast assortment of proteins found in all living cells. The process of linking amino acids into proteins begins in the cell nucleus. Web within a protein, multiple amino acids are linked together by.
Amino Acids BioNinja
Web amino acids are organic compounds containing two functional groups, i.e. And i'd walk straight passed the nudes without even looking. Protein may contain one or. Higher levels of protein structure are described in figure below. The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino.
Amino Acids Nicoptere
A protein consists of one or more polypeptide chains. A longer chain of linked amino acids (51 or more) is a polypeptide. Web what are long chains of amino acids called? A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. The lowest level, a protein’s primary structure, is its sequence of amino acids.
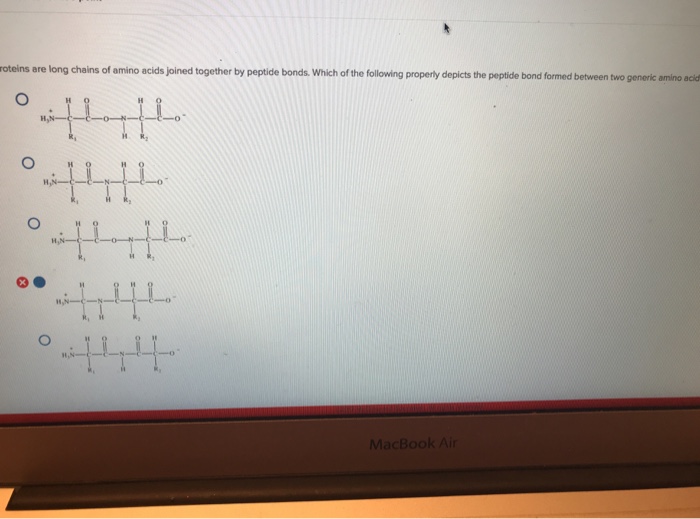
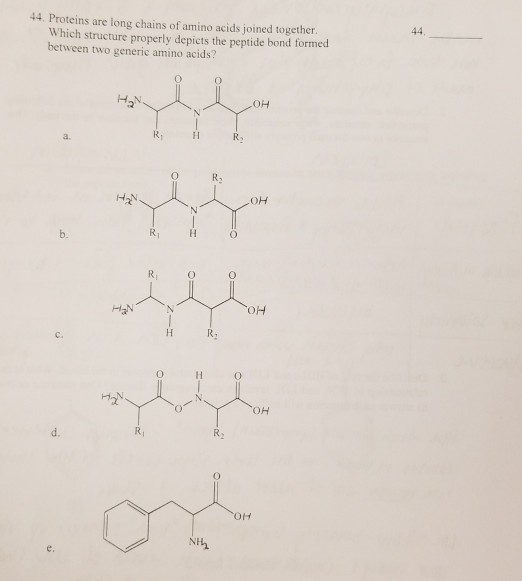
Solved 44. Proteins are long chains of amino acids joined
Web amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein. Web amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side chain. The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. Web all of the proteins on the face of.
Amino Acids Chemistry, Biochemistry & Nutrition Amit Kessel Ph.D
Higher levels of protein structure are described in figure below. These short chains are called peptides. To build a protein molecule, your body undergoes a series of reactions during a process called protein synthesis. Web amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side.
[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary
The process of linking amino acids into proteins begins in the cell nucleus. Review the general structure of an amino acid in the biological molecules chapter of your text. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon called the. Polypeptides which have a molecular mass of 10,000 da or more are called proteins. Web the amino acid sequence.
Polypeptide Chain Structure The Peptide Bond Polypeptide chain
Some proteins function as enzymes, some as antibodies, while others provide structural support. So, imagine each amino acid as a pearl strung together with other pearls in a long necklace. Web amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side chain. The α carbon,.
Proteins are chains of amino acids. A) Structure of a typical amino
The α carbon, carboxylic acid, and amino. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. At one end, the polypeptide has a free amino group, and this end is called the amino terminus (or. Protein may contain one or. They fold, they coil, they twist.
Solved Proteins. Long chains of amino acids are called
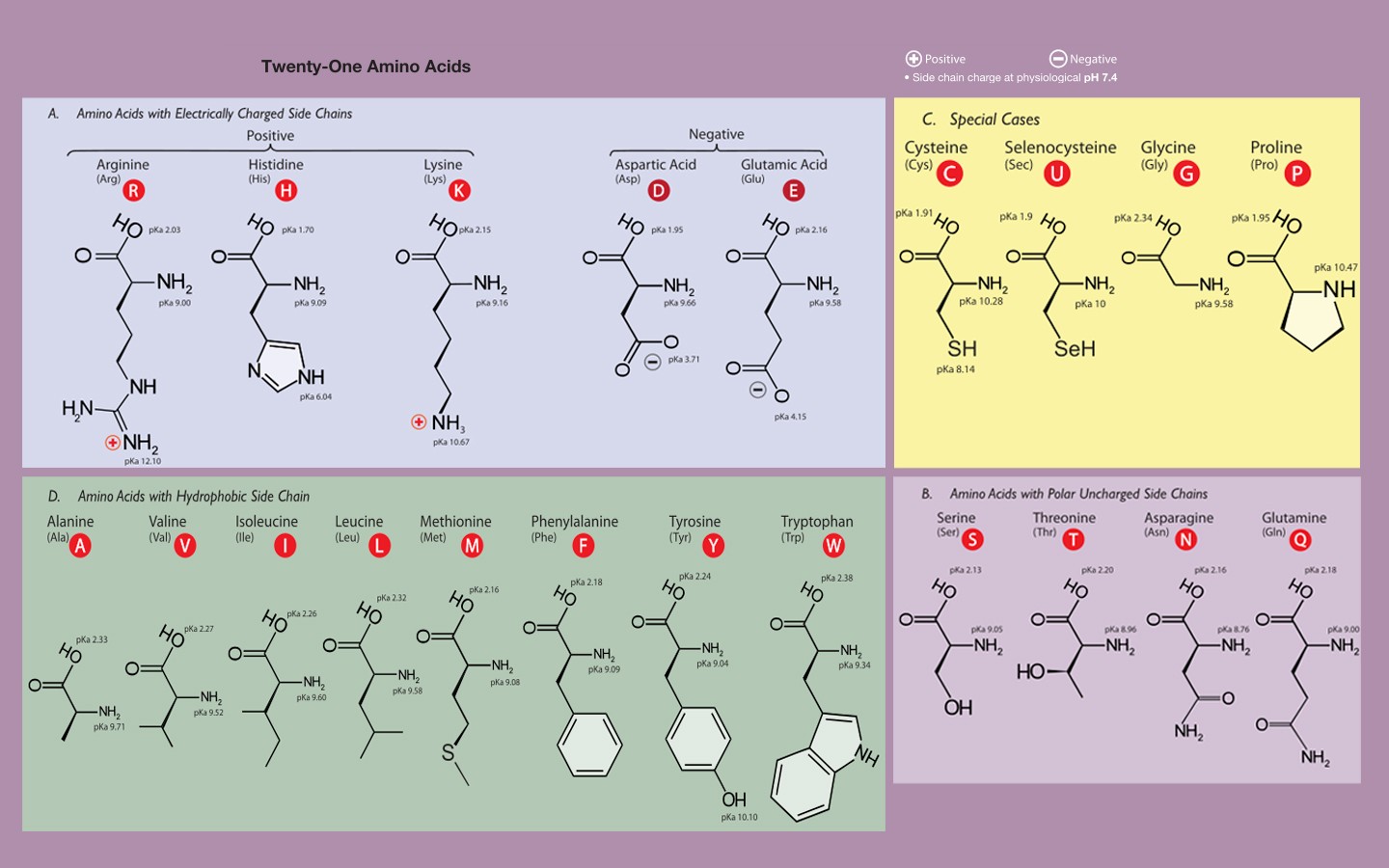
Twenty different amino acids are used to build a protein. Web amino acids are organic molecules that, when linked together with other amino acids, form a protein. Web all amino acids have the same basic structure, shown in figure 2.1. The start of the sequence is always at the amino terminal and the end being the carboxy terminal. Chains of.
Amino Acids Public Domain Images
Web proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. And i'd walk straight passed the nudes without even looking. Web because of the structure of the amino acids, a polypeptide chain has directionality, meaning that it has two ends that are chemically distinct from one.
Peptide Bond Between Amino Acids.
How the protein is built is based on. Amino (−nh 2) and carboxylic (−cooh −) and an organic side chain. Web amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group, an acidic carboxyl group, and a unique organic side chain. Long chains of amino acids are called polypeptide chains.
A Protein May Have Up To Four Levels Of Structure.
When these chains form the proper shape, they become a functional protein. Web proteins are made up of hundreds or thousands of smaller units called amino acids, which are attached to one another in long chains. If they were sculptures i would go to the museum every day just to look at them. The lowest level, a protein’s primary structure, is its sequence of amino acids.
Web When Amino Acids Bind Together, They Form A Long Chain Called A Polypeptide.
A longer chain of linked amino acids (51 or more) is a polypeptide. To build a protein molecule, your body undergoes a series of reactions during a process called protein synthesis. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Review the general structure of an amino acid in the biological molecules chapter of your text.
A Protein Consists Of One Or More Polypeptide Chains.
Linked together in long chains called polypeptides, amino acids are the building blocks for the vast assortment of proteins found in all living cells. And i'd walk straight passed the nudes without even looking. Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Web because of the structure of the amino acids, a polypeptide chain has directionality, meaning that it has two ends that are chemically distinct from one another.


![[LS16] Sugar to Carbon Molecules Biology Dictionary](https://biologydictionary.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Common-amino-acids.jpg)



