3X Y 5 In Slope Intercept Form
3X Y 5 In Slope Intercept Form - Y = mx + b. The number before the x variable is the slope, so. Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Subtract from both sides of the. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3). Subtract from both sides of the. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Divide each term in by and simplify.
Subtract from both sides of the equation. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3). Subtract from both sides of the. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. Divide each term in by and simplify. Web recall that the slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y y over the change in x x between any two points on the line: #m# is the slope of the line. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Subtract from both sides of the.
(0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Divide each term in by and simplify. The number before the x variable is the slope, so. #m# is the slope of the line. Subtract from both sides of the. #y = mx + b# where: Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3. Web recall that the slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y y over the change in x x between any two points on the line: Subtract from both sides of the.
Choose the best description for graphing y = 3x 5 using the slope and
The number before the x variable is the slope, so. Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3. Y = mx + b. Subtract from both sides of the equation. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3).
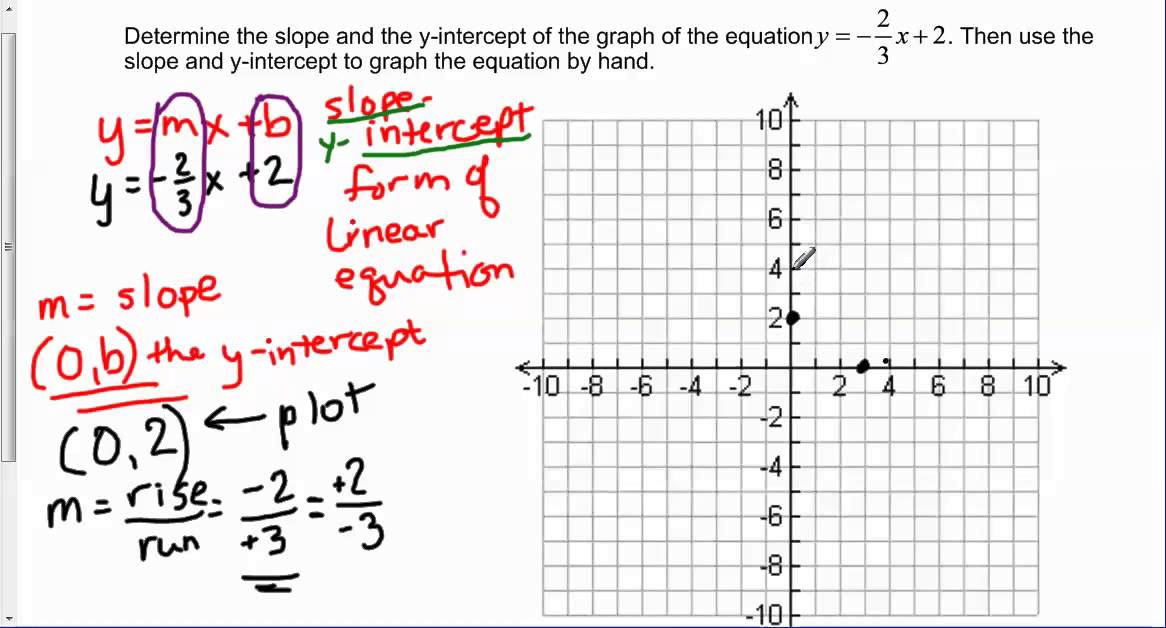
Determine the slope and yintercept of y = 2/3x + 2 the graph the
#m# is the slope of the line. Subtract from both sides of the equation. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3). Subtract from both sides of the. Subtract from both sides of the.
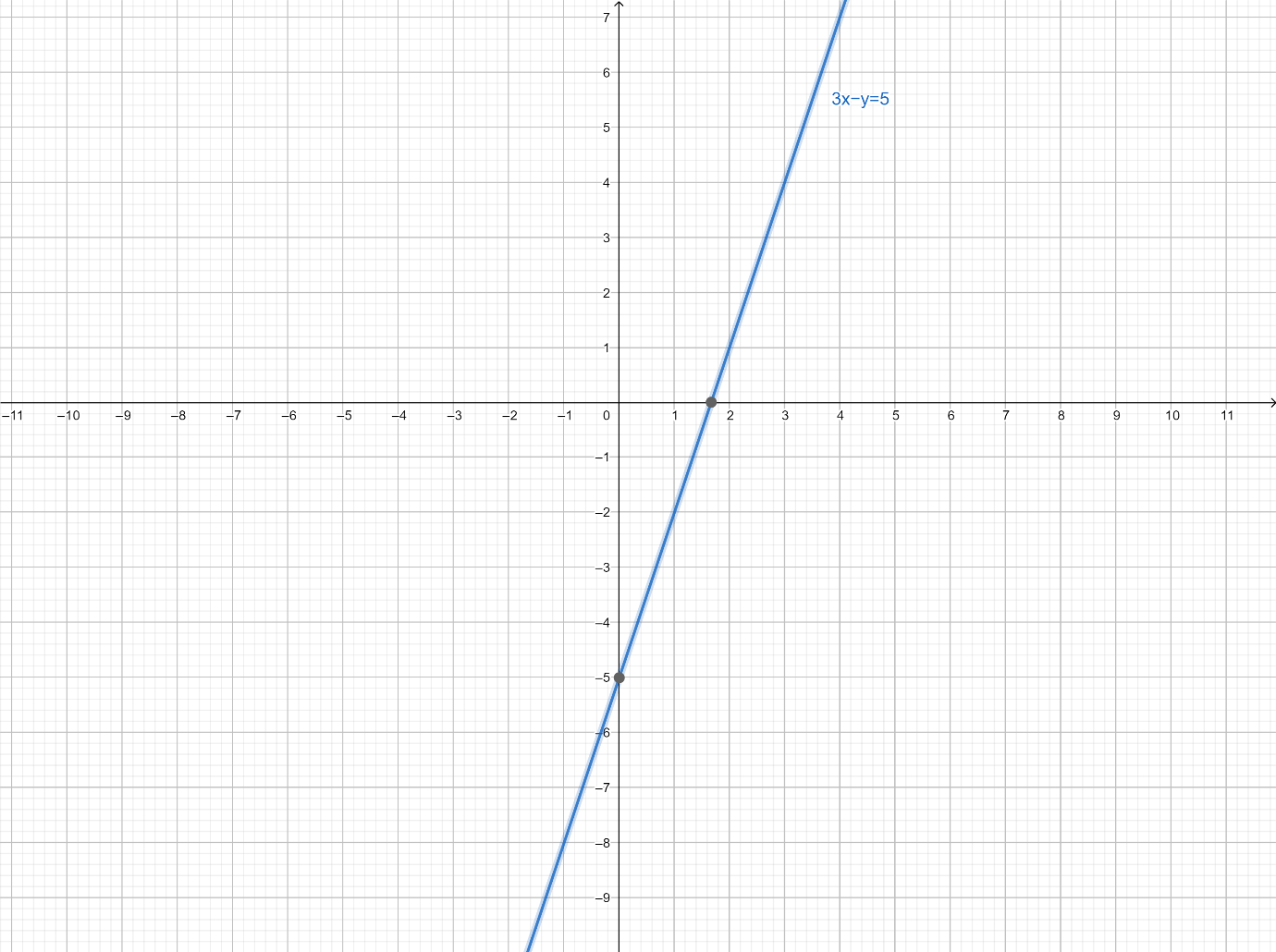
How do you find the slope and intercept of 3x y 5 class 11 maths CBSE
Subtract from both sides of the equation. Subtract from both sides of the. Y = mx + b. Divide each term in by and simplify. Web recall that the slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y y over the change in x x between any two points on the line:
Chapter 5 SlopeIntercept Form
Web recall that the slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y y over the change in x x between any two points on the line: Subtract from both sides of the. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as.
Graphing a linear equation in slopeintercept form y=3x5 YouTube
The number before the x variable is the slope, so. Divide each term in by and simplify. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3).
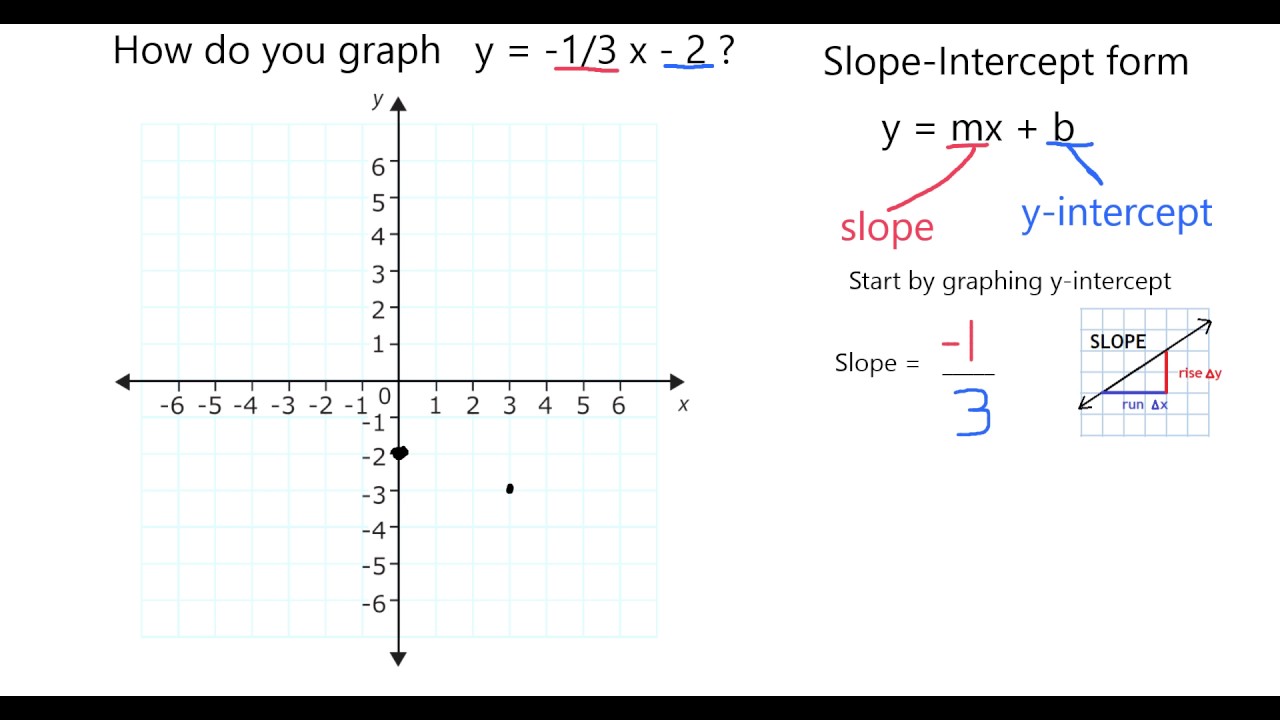
Graph in slope intercept form y = 1/3 x 2 YouTube
Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Subtract from both sides of the. Subtract from both sides of the. Y = mx + b. Divide each term in by and simplify.
Chapter 5 SlopeIntercept Form
Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. #y = mx + b# where: Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. Y = mx + b.
How do you graph y=3x+5 using slope intercept form? Socratic
#m# is the slope of the line. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3. Divide each term in by and simplify. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y =.
Write In Slope Intercept Form 5x 3y 9 slideshare
Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3). Subtract from both sides of the. #m# is the slope of the line. Divide each term in by and simplify. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,.
Determine the slope and yintercept of y = 3x + 5 and then graph the
Subtract from both sides of the equation. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what. Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. Y = mx + b. Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3.
#Y = Mx + B# Where:
Subtract from both sides of the. Therefore, this is the slope between the points (0,3). Y = mx + b. Rearrange the equation by subtracting what.
Subtract From Both Sides Of The.
The number before the x variable is the slope, so. Subtract from both sides of the equation. Web recall that the slope of a line is the ratio of the change in y y over the change in x x between any two points on the line: Thus, reorganising as y = −3x + 5, we get the slope as −3.
#M# Is The Slope Of The Line.
Also, using the same explicit form we can calculate the y intercept (where x = 0 ), as y = 5,. Divide each term in by and simplify. (0,0) ( 0, 0) any line can be graphed using two points. Subtract from both sides of the.