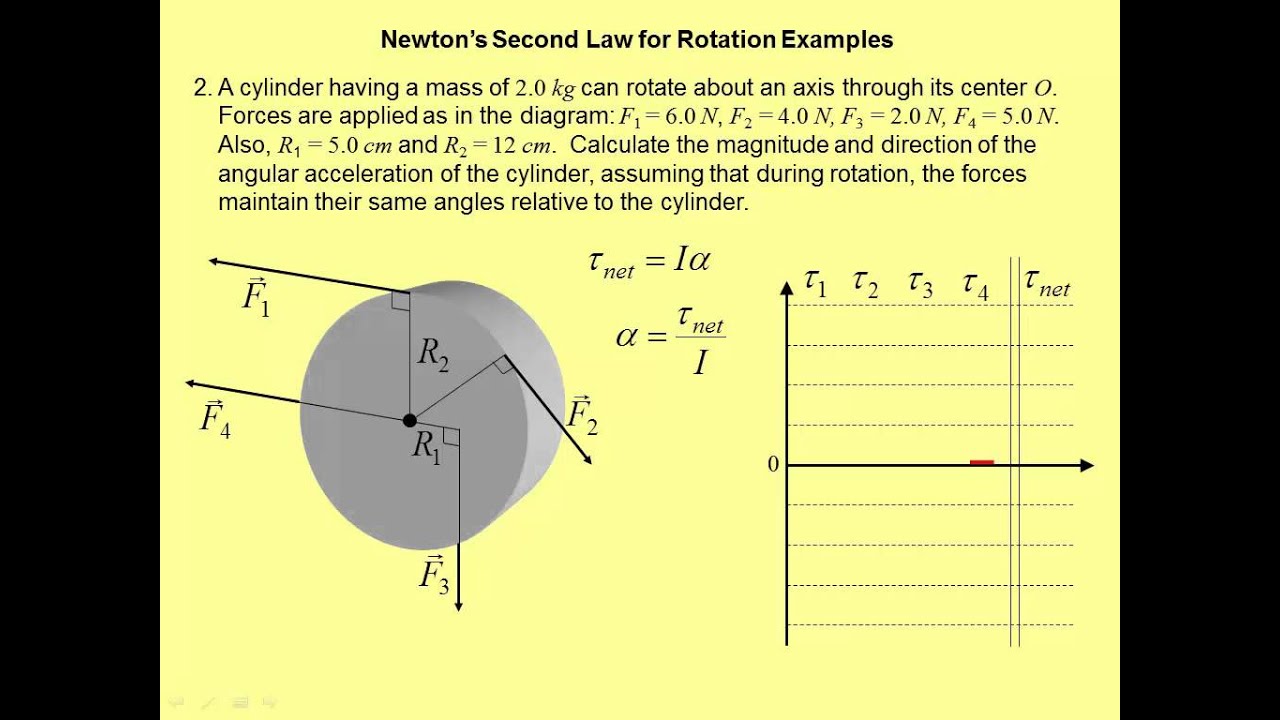
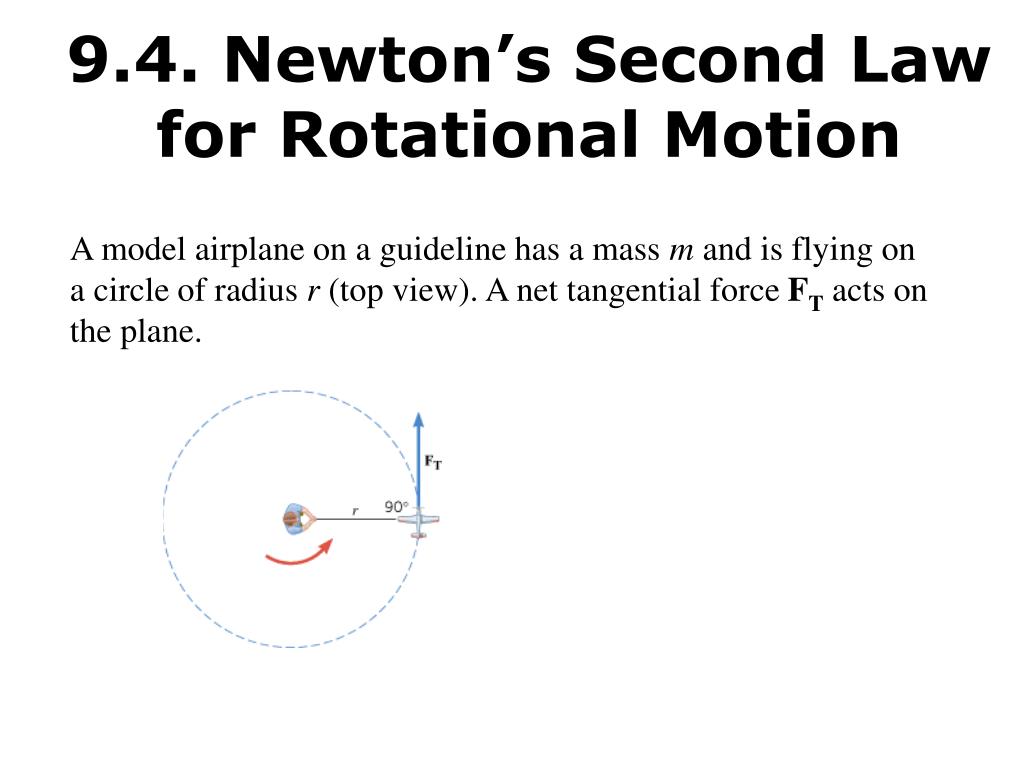
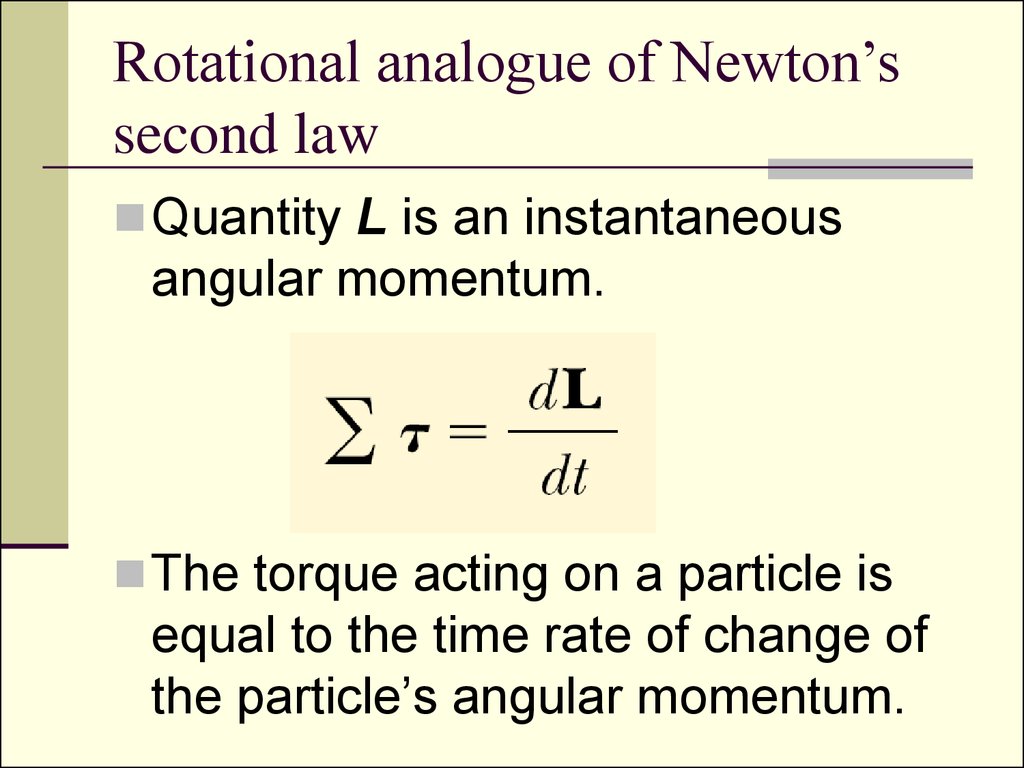
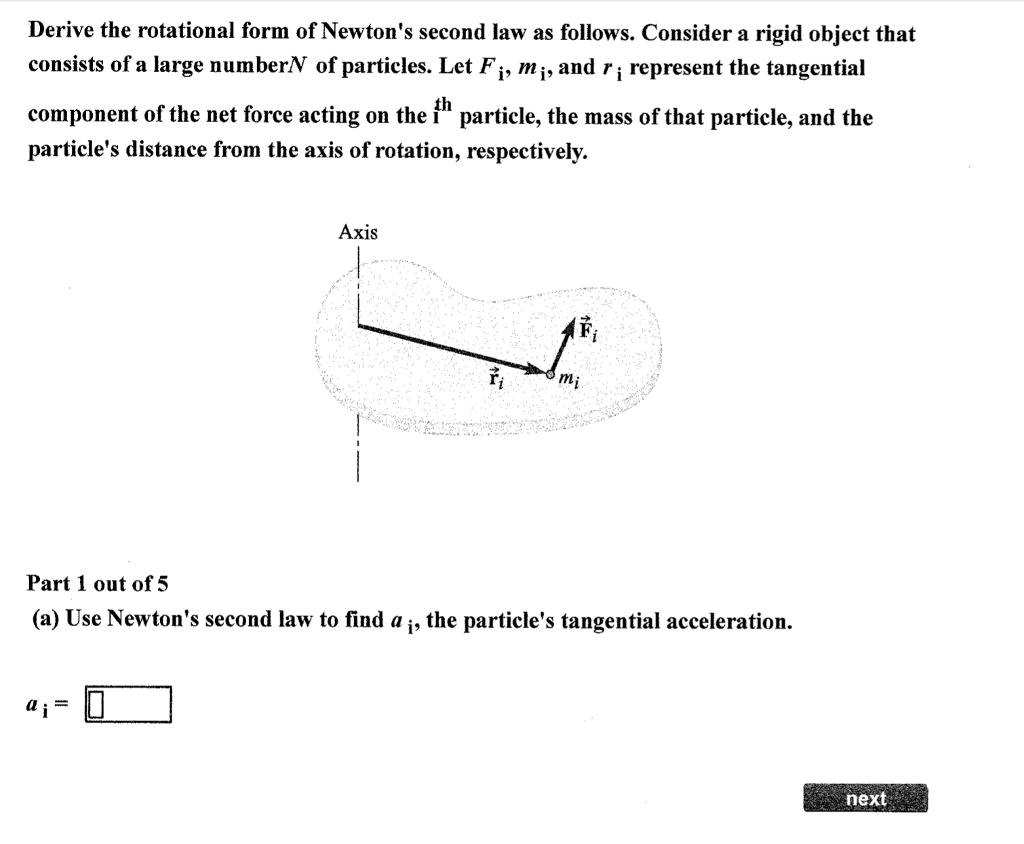
Rotational Form Of Newton's Second Law
Rotational Form Of Newton's Second Law - Web newton's second law for rotation what is the angular acceleration produced by applying a torque to an object? Web identifying the first term on the left as the sum of the torques, and mr2 m r 2 as the moment of inertia, we arrive at newton’s second law of rotation in vector form: Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. Web v t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. This is called the equation for rotational dynamics. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form. Web 9.5k views 4 years ago. Web newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. Web newton’s second law for rotation, [latex]\sum _{i}{\tau }_{i}=i\alpha[/latex], says that the sum of the torques on a rotating system about a fixed axis equals the product of the. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form.
A basic rotational form of newton’s second law problem with only one force. Rotation the relationship between the net external torqueand the angular accelerationis of the same form as newton's second lawand is sometimes. Web v t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. Where fnet (or ∑ f) is the net external force, m is the mass of the system, and a is the. Web newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. With this equation, we can solve a whole class of problems involving force. Web newton’s second law for rotation if more than one torque acts on a rigid body about a fixed axis, then the sum of the torques equals the moment of inertia times the angular. Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us how to relate torque, moment of inertia, and rotational kinematics. Web mathematically, the second law is most often written as. Web 9.5k views 4 years ago.
Web v t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it. Web mathematically, the second law is most often written as. Rotation the relationship between the net external torqueand the angular accelerationis of the same form as newton's second lawand is sometimes. Web 9.5k views 4 years ago. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form. With this equation, we can solve a whole class of problems involving force. Where fnet (or ∑ f) is the net external force, m is the mass of the system, and a is the. It states that the time rate of change of the momentum of a body. Web newton's second law for rotation what is the angular acceleration produced by applying a torque to an object? A basic rotational form of newton’s second law problem with only one force.
Newton's 2nd Law for Rotation Examples YouTube
Web newton’s second law for rotation, [latex]\sum _{i}{\tau }_{i}=i\alpha[/latex], says that the sum of the torques on a rotating system about a fixed axis equals the product of the. Web v t e newton's laws of motion are three basic laws of classical mechanics that describe the relationship between the motion of an object and the forces acting on it..
PPT 9.4. Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion PowerPoint
Web newton's second law for rotation what is the angular acceleration produced by applying a torque to an object? This is called the equation for rotational dynamics. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form. Web equation 10.25 is newton’s second law for rotation and tells us.
Solved Derive the rotational form of Newton's second law as
Web identifying the first term on the left as the sum of the torques, and mr2 m r 2 as the moment of inertia, we arrive at newton’s second law of rotation in vector form: A basic rotational form of newton’s second law problem with only one force. Web newton’s second law for rotation, [latex]\sum _{i}{\tau }_{i}=i\alpha[/latex], says that the.
Rotation of rigid bodies. Angular momentum and torque. Properties of
Web identifying the first term on the left as the sum of the torques, and mr2 m r 2 as the moment of inertia, we arrive at newton’s second law of rotation in vector form: Web newton's second law determines the form of the atom dynamics, subject to initial conditions. Web v t e newton's laws of motion are three.
Solved Derive the rotational form of Newton's second law as
Web looking at the form of newton's second law shown above, we see that the acceleration is proportional to the net force, σ f \sigma f σ f \sigma, f, and is inversely proportional to. The solutions lead to the trajectory r ( t ), and they also determine the. This is an ap physics 1 topic. Web identifying the.
Newton's 2nd Law for Rotation YouTube
Web newton’s second law for rotation, [latex]\sum _{i}{\tau }_{i}=i\alpha[/latex], says that the sum of the torques on a rotating system about a fixed axis equals the product of the. Web looking at the form of newton's second law shown above, we see that the acceleration is proportional to the net force, σ f \sigma f σ f \sigma, f, and.
Rotational Version of Newton's Second Law YouTube
The solutions lead to the trajectory r ( t ), and they also determine the. This is an ap physics 1 topic. F net = m a or σ f = m a, 4.2. This is called the equation for rotational dynamics. Web looking at the form of newton's second law shown above, we see that the acceleration is proportional.
PPT Ch 9. Rotational Dynamics PowerPoint Presentation ID277645
The solutions lead to the trajectory r ( t ), and they also determine the. Web mathematically, the second law is most often written as. This is an ap physics 1 topic. Web newton's second law determines the form of the atom dynamics, subject to initial conditions. Web 9.5k views 4 years ago.
Rotational Form of Newton's Second Law Introduction YouTube
Web 19 rows we can use newton’s second law to find the linear acceleration of the ball. Web identifying the first term on the left as the sum of the torques, and mr2 m r 2 as the moment of inertia, we arrive at newton’s second law of rotation in vector form: Web a very basic introduction to the rotational.
AP Physics Rotational Motion Torque and Newton's Second Law YouTube
Web newton's second law for rotation what is the angular acceleration produced by applying a torque to an object? The solutions lead to the trajectory r ( t ), and they also determine the. Web newton’s second law for rotation if more than one torque acts on a rigid body about a fixed axis, then the sum of the torques.
Web 9.5K Views 4 Years Ago.
Web identifying the first term on the left as the sum of the torques, and mr2 m r 2 as the moment of inertia, we arrive at newton’s second law of rotation in vector form: Web newton’s second law for rotation if more than one torque acts on a rigid body about a fixed axis, then the sum of the torques equals the moment of inertia times the angular. Newton's second law states that the angular acceleration is. With this equation, we can solve a whole class of problems involving force.
Web V T E Newton's Laws Of Motion Are Three Basic Laws Of Classical Mechanics That Describe The Relationship Between The Motion Of An Object And The Forces Acting On It.
This is an ap physics 1 topic. This is called the equation for rotational dynamics. Web newton's second law determines the form of the atom dynamics, subject to initial conditions. Web newton’s second law for rotation if more than one torque acts on a rigid body about a fixed axis, then the sum of the torques equals the moment of inertia times the angular.
Rotation The Relationship Between The Net External Torqueand The Angular Accelerationis Of The Same Form As Newton's Second Lawand Is Sometimes.
Web newton’s second law is a quantitative description of the changes that a force can produce on the motion of a body. Web when rotations about a fixed axis are the relevant motion produced, the concept of torque is the relevant quantity for producing changes in the rotation rate. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form. Web newton's second law for rotation what is the angular acceleration produced by applying a torque to an object?
Web Looking At The Form Of Newton's Second Law Shown Above, We See That The Acceleration Is Proportional To The Net Force, Σ F \Sigma F Σ F \Sigma, F, And Is Inversely Proportional To.
Web mathematically, the second law is most often written as. Web a very basic introduction to the rotational form of newton’s second law of motion by way of its translational form. F net = m a or σ f = m a, 4.2. The solutions lead to the trajectory r ( t ), and they also determine the.